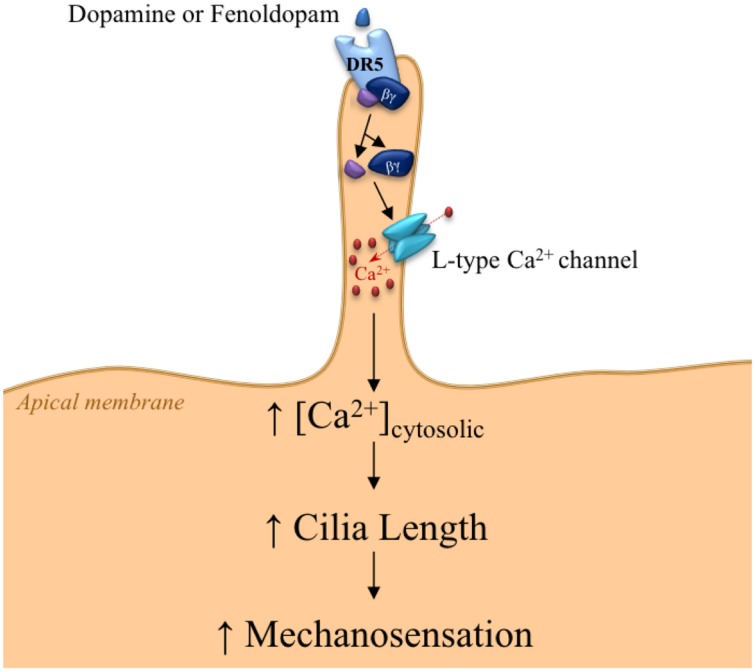
Figure 2.
Proposed mechanism for DR5 signaling within the primary cilium. The signaling within primary cilia is triggered by the chemosensory function of primary cilia through DR5 activation, resulting in dissociation of Gα and Gβ γ subunits. The Gβ γ subunit activates L-type calcium channels, thereby increasing cilioplasm calcium concentration. Calcium-induced cilia elongation provides greater sensitivity to fluid-shear stress.