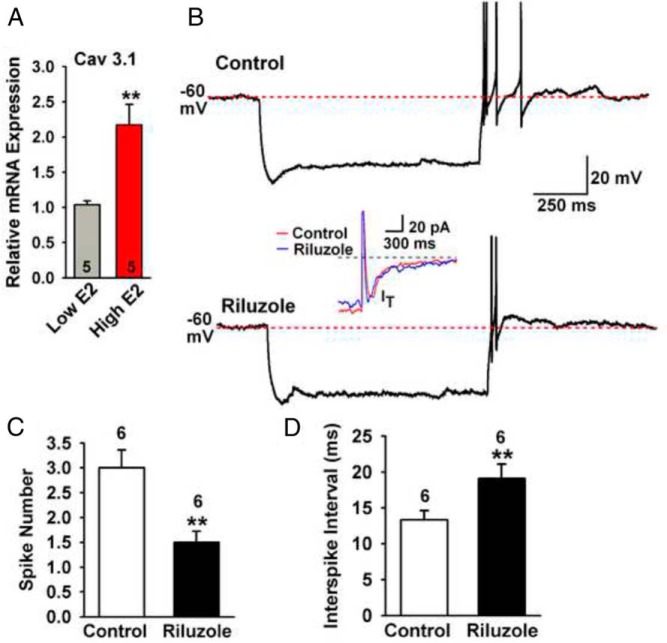
Figure 4.
INaP modulates T-type calcium channel-mediated rebound burst firing. A, qPCR measurements of CaV3.1 mRNA in AVPV/PeN Kiss1 neuronal pools (three pools per animal) from low-E2 and high-E2 mice (n = 5 animals in each group). **, P < .01, Student's t test. B, Representative recordings showing that in control conditions hyperpolarizing a cell to −95 mV for 1 second from −60 mV induced rebound burst firing with four action potentials (upper trace); however, in the presence of riluzole (10 μM), the same hyperpolarization from −60 mV induced rebound burst firing with only two action potentials, and the interspike interval from the first to the second action potential increased from 12 milliseconds to 18 milliseconds. The inset (middle trace) shows that riluzole had no effect on the T-type calcium current amplitude. C and D, Summary of the effects of riluzole on the number of action potentials (spikes) in the rebound burst and interspike intervals. **, P < .01, n = 6; Student's t test.