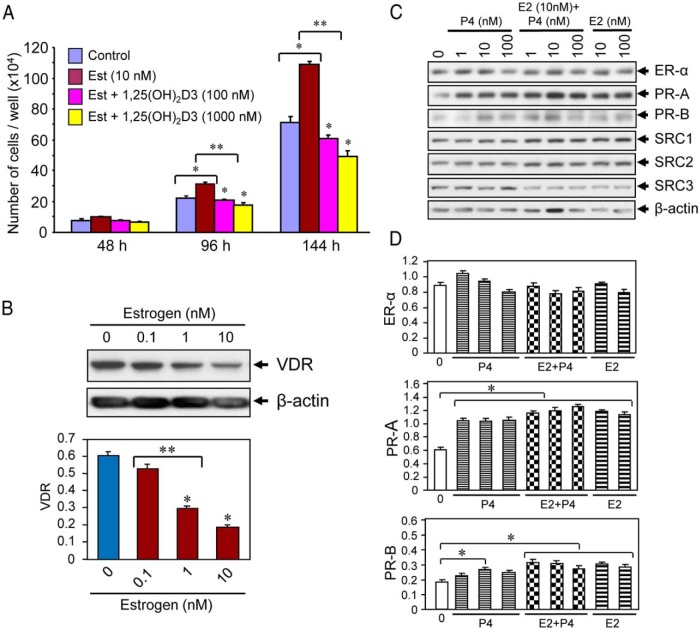
Figure 2.
Effect of 1,25(OH)2D3 on estrogen-induced proliferation of cultured human UF cells. A, HuLM cells (5000 cells/well) in 12-well plates were cultured in phenol free smooth muscle basal medium containing 5% fetal bovine serum. Cells were treated with 10 nm estrogen with or without varying doses of 1,25(OH)2D3 (100 and 1000 nm) for 48, 96, and 144 hours. Cultures were replenished every other day with fresh conditioned media. Cells were trypsinized at each time point and counted using cell-counting chamber slides. Each data point is the mean ± SD of triplicate wells (n = 3). *, P < .05 as compared to the corresponding control. **, P < .05 as compared to treatment points. B, Estrogen treatment reduced the levels of VDR in HuLM cells. HuLM cells (0.7 × 106) were cultured in 60-mm dishes, serum starved in phenol free DMEM/F12 medium, and treated with increasing doses of estrogen for 48 hours, as indicated. Equal amounts of each cell lysate were analyzed by Western blot using polyclonal anti-VDR antibody. Western blot with anti-β-actin antibody was used as the loading control. The intensity of each protein band was quantified and normalized to β-actin, and relative values were used to generate graphic data. *, P < .05 compared to corresponding control. **, P < .05 indicates the significance between consecutive doses. C, Estrogen or progesterone treatment induced PRs in HuLM cells. HuLM cells were cultured and serum starved as described above. Cells were treated with different doses of estrogen or progesterone or in combination (estrogen and progesterone together) for 48 hours as indicated. Cell lysates were analyzed by Western blot using anti-ER-α, anti-PR-A, anti-PR-B, anti-SRC1, anti-SRC2, and anti-SRC3 antibodies. Western blot with anti-β-actin antibody was used as the loading control. D, The intensities of above ER-α, PR-A, and PR-B protein bands were quantified and normalized to β-actin, and relative values were used to generate graphic data. *, P < .05 as compared to the corresponding control.