Fig. 3.
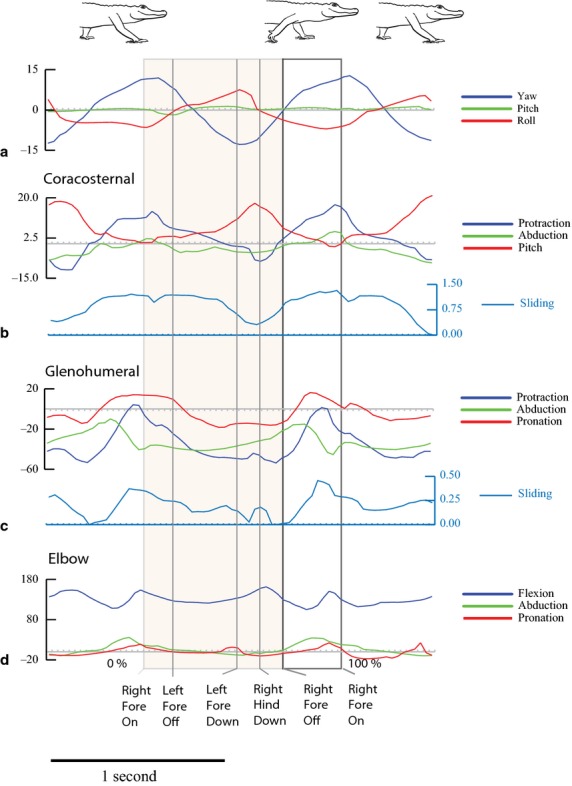
Two representative strides for Alligator1 walking at 0.31 m s−1 with stride events marked. The shaded area is stance phase. Colors match Fig. 2 joint coordinate systems. (a) Yaw, pitch and roll of the dorsal scute markers in the shoulder region. Positive yaw is to the left; negative yaw is to the right. Positive pitch is nose up; negative pitch is nose down. Positive roll is to the left; negative roll is to the right. The scute marker movements are a proxy for the vertebral reference frame. (b) Coracosternal movements. Protraction is positive and retraction is negative (blue). Adduction is positive and abduction is negative. Positive pitch moves the dorsal end of the scapula posteriorly and negative pitch moves the dorsal scapula anteriorly. Cranial sliding is positive and caudal sliding is negative. (c) Glenohumeral protraction is positive and retraction is negative. Abduction of the humerus above the horizontal plane is positive and adduction below the horizontal plane is negative. Pronation is negative and supination is positive. Cranial sliding is positive and caudal sliding is negative. (d) Elbow extension is positive. Flexion refers to a decreasing angle of movement. Abduction is a lateral deviation relative to the humeral condyles and is positive. Adduction is a medial deviation relative to the humeral condyles and is negative. Pronation is negative and supination is positive.
