Fig. 3.
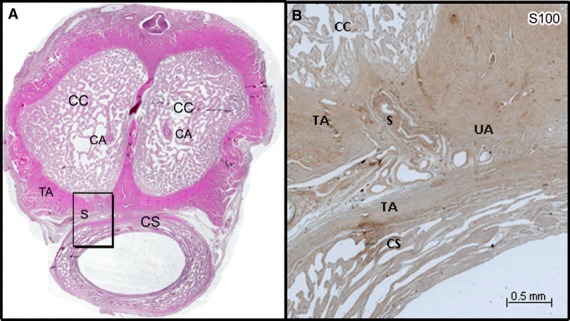
(A) Histological section of the penis of a 68-year-old man stained by HE and scanned at high resolution (3200 dpi). (B) Microscopic aspect (×10) of the shunt (S) between the CA and the UA (frame in A) immunostained with anti-protein S100. The shunt came from the CA, passed on the ventral surface of the tunica albuginea (TA) of the corpora cavernosa (CC) to join UA located on the dorsal surface of the corpus spongiosum (CS) between the two tunicae albugineae (TA) and not in the CS, hence our use of the term ‘cavernosal urethral shunt’.
