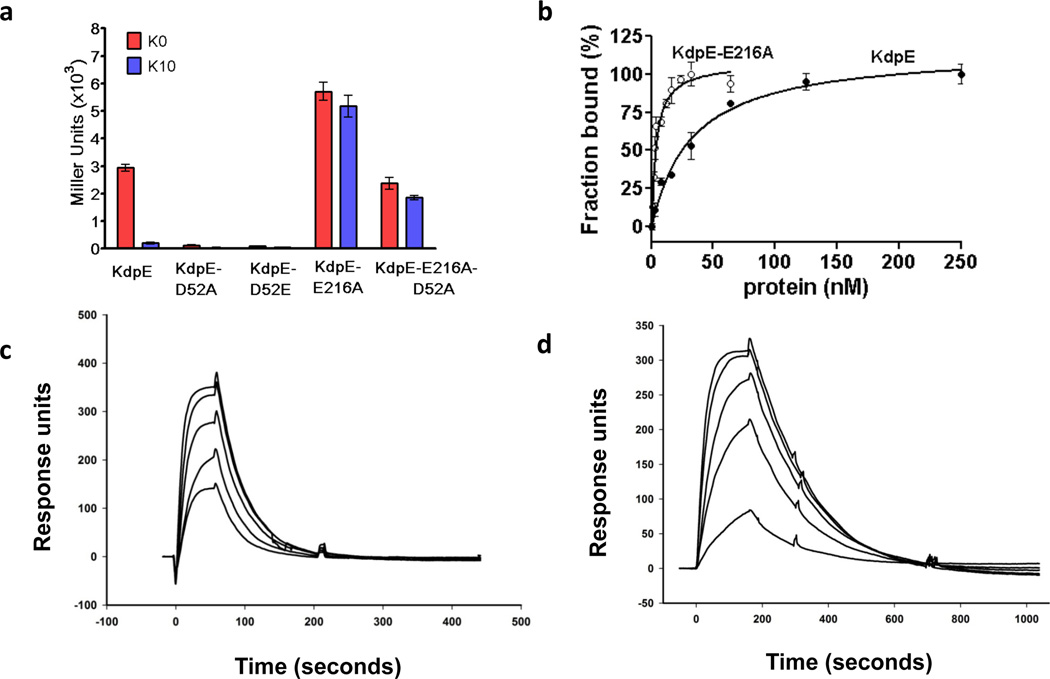
Figure 1. Characterization of the RR KdpE and its variants.
a, β-Galactosidase expression in E. coli cells co-expressing histidine kinase KdpD with wild-type KdpE, KdpE-E216A, double substituent KdpE-E216A-D52A, or inactive KdpE-D52A and KdpE-D52E in inducing media without K+ ( ) or in 10 mM K+ (
) or in 10 mM K+ ( ). b, Analysis of binding of KdpE (black circles) and KdpE-E216A (white circles) to DNA by fluorescence anisotropy; estimated dissociation constants were 30 ± 4.0 nM and 3.5 ± 0.5 nM, respectively. Error bars represent SEM of three independent measurements. c and d, Surface plasmon resonance analysis. The binding to DNA immobilized on a chip was analyzed by injecting various concentrations of (c) KdpE (50 – 300 nM) and (d) KdpE-E216A (10 – 50 nM).
). b, Analysis of binding of KdpE (black circles) and KdpE-E216A (white circles) to DNA by fluorescence anisotropy; estimated dissociation constants were 30 ± 4.0 nM and 3.5 ± 0.5 nM, respectively. Error bars represent SEM of three independent measurements. c and d, Surface plasmon resonance analysis. The binding to DNA immobilized on a chip was analyzed by injecting various concentrations of (c) KdpE (50 – 300 nM) and (d) KdpE-E216A (10 – 50 nM).