Figure 1.
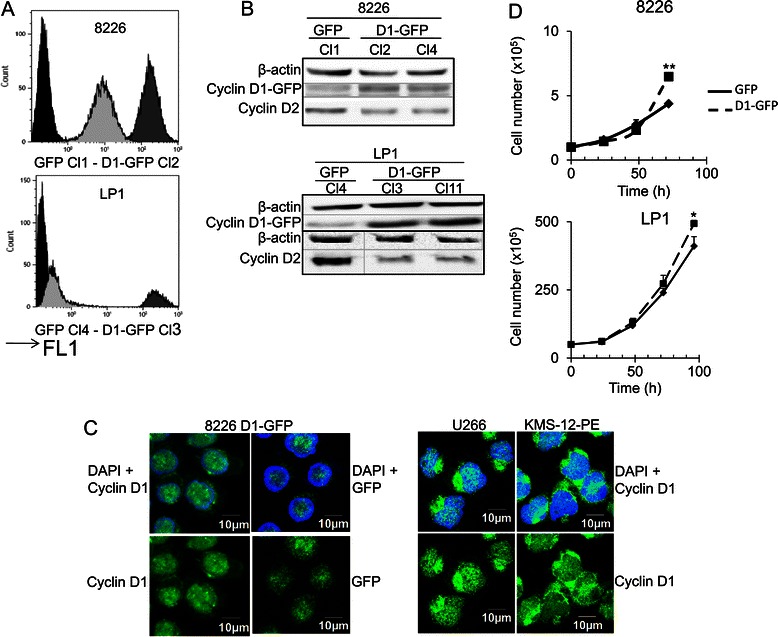
Cyclin D1 is expressed in 8226- and LP1-derived clones. A. The GFP fluorescence (FL1) of parental cells and the clones derived from them were analyzed by flow cytometry. Representative profiles are shown from the selected clones: in black, parental cells; light gray: cyclin D1-GFP clone; dark gray: GFP clone. B. Whole-cell proteins extracts were obtained from GFP- and cyclin D1-GFP-expressing cells, and subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with the indicated Abs. An Ab directed against β-actin was used as loading control. The 8826 D1-GFP Cl2 and LP1 D1-GFP Cl3 clones were used for the experiments shown in parts A and D of this figure and for subsequent investigations. C. 8226 cells expressing exogenous cyclin D1 or U266 and KMS-12-PE cells expressing endogenous cyclin D1 were stained with anti-cyclin D1 Ab then with AlexaFluor 633-conjugated anti-mouse IgG (in green) and couterstained with DAPI (in blue). Slides were analyzed by confocal microscopy (Fluoview microscope). D. Clones presented in A were used to seed complete medium at a density of 2 × 105 cells/ml, and their growth was evaluated daily, over a three- or four-day period, by direct counting after trypan blue staining. The experiment was carried out three times in triplicate. The mean number of living cells is shown, together with the SD. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 in Student’s t-test.
