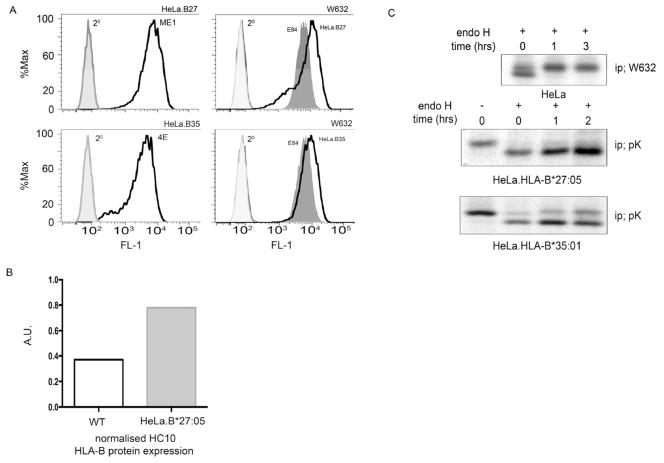
Figure 1.
HLA-B27 expression and maturation in HeLa cells; (A) HLA-B27 and –B35 are expressed efficiently at the cell surface. HeLa.B27.Sv5 and –B35.Sv5 were analysed by flow cytometry with antibodies ME1 (top left) and 4E (bottom left) respectively. HeLa.B27, -B35 and mock transfected control E84 express W632 reactive MHC class I molecules. (B) Quantitation of HLA-B alleles using HC10 antibody signal reveals approximately twice as much HLA-B expression in HeLa.B27.Sv5 compared to wild type HeLa cells. (C) HeLa cells process MHC class I molecules efficiently. Pulse chase analysis of endogenous MHC class I molecules using antibody W632 followed by endo H digestion reveals that MHC class I molecules mature within 1hr (top panel). Pulse chase of HLA-B27.Sv5 using the anti-Sv5 antibody pK reveals little endo H resistant material being acquired during 2 hrs of chase (middle panel). Control HLA-B35.Sv5 exhibit a rapid acquisition of endo H resistance in HeLa cells (bottom panel).