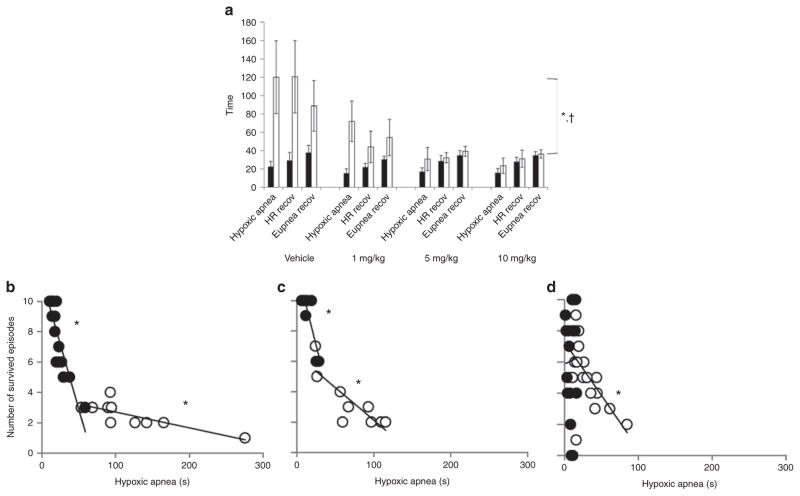
Figure 3.
Effects of Pet-1-deficiency and caffeine on autoresuscitation. (a) Summary of autoresuscitation variables in wild-type mouse pups and their Pet-1−/− littermates. Group data showing the average duration of hypoxic apnea and time required to recover heart rate (HR recov) and eupnea (Eupnea recov) across all episodes of environmental asphyxia for wild-type (black bars) and Pet-1−/− littermates (open bars) receiving an i.p. injection of either vehicle or 1, 5, or 10 mg/kg of caffeine. *Significant effect of genotype (P < 0.001 for all variables); †significant genotype × caffeine interaction (P < 0.001 for all variables). The data shown are mean values ± 95% confidence intervals. (b–d) Relationship between number of asphyxic episodes survived and the duration of apnea in wild-type mice (closed circles) and Pet-1−/− mice (open circles), treated with vehicle (b; R2= 0.76 (wild-type) and 0.78 (Pet-1−/−)), 1 mg/kg caffeine (c; R2 = 0.75 (wild-type) and 0.70 (Pet-1−/−)), or 5 or 10 mg/kg caffeine (grouped) (d; R2 < 0.001 (wild-type) and 0.34 (Pet-1−/−)). *Significant relationships, P < 0.05. Data points represent individual animals.