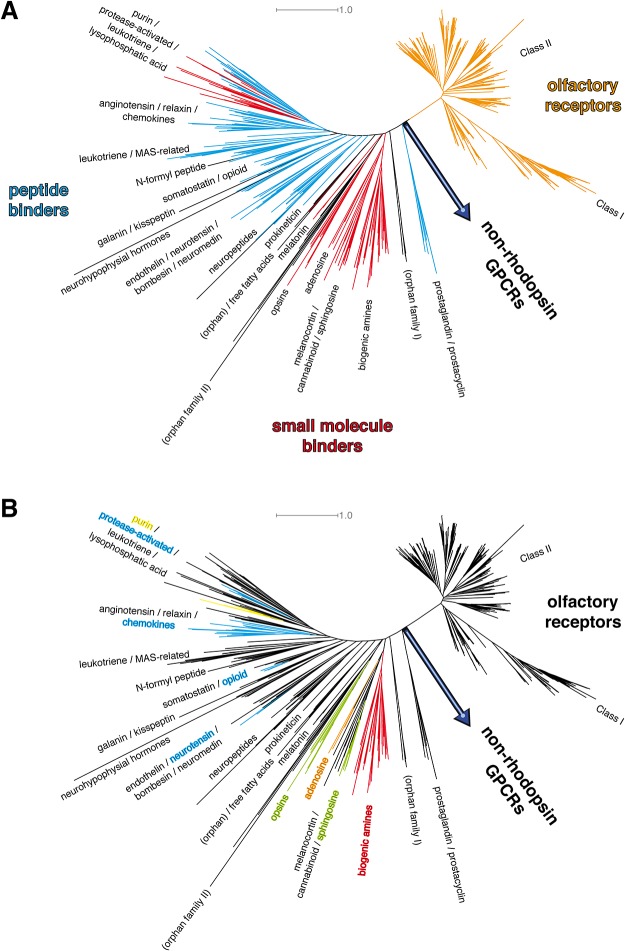
Fig 2. Phylogenetic analysis of the full rhodopsin-like GPCR crystal structure set.
Phylogenetic analysis of known human rhodopsin-like GPCR protein 7TM sequences after assignment of the transmembrane helices by alignment of the full scope of human GPCR protein sequences with the respective 7TM sequences from receptors with available x-ray structures. A: classification according to known ligand binding. The tree shows three major branches: olfactory receptors (in orange), small molecule binders (red), peptide binders (cyan). Orphan receptors in black. Olfactory receptors form a subclass of their own within the rhodopsin-like class. Small molecule binding GPCRs form a clear cluster. Peptide receptors cluster at the left end of the tree, starting with the neuropeptides subbranch. A 2nd set of small ligand receptors, which are the purine, leukotriene, and the free fatty acids receptors, mixes with protease-activated receptors. B: classification according to ligand properties as found in X-ray crystallography structures. Color scheme like in Fig 1. Known crystallized ligands can be subdivided into hydrophobic ligands (green), biogenic amines (red), hydrophilic ligands (orange), peptides (cyan), and purines (yellow). The small molecule binding receptor families closest to the common node with non-rhodopsin GPCRs are hydrophobic ligand GPCRs. The overall picture is in good agreement with the one found for the crystallized GPCRs from Fig 1.