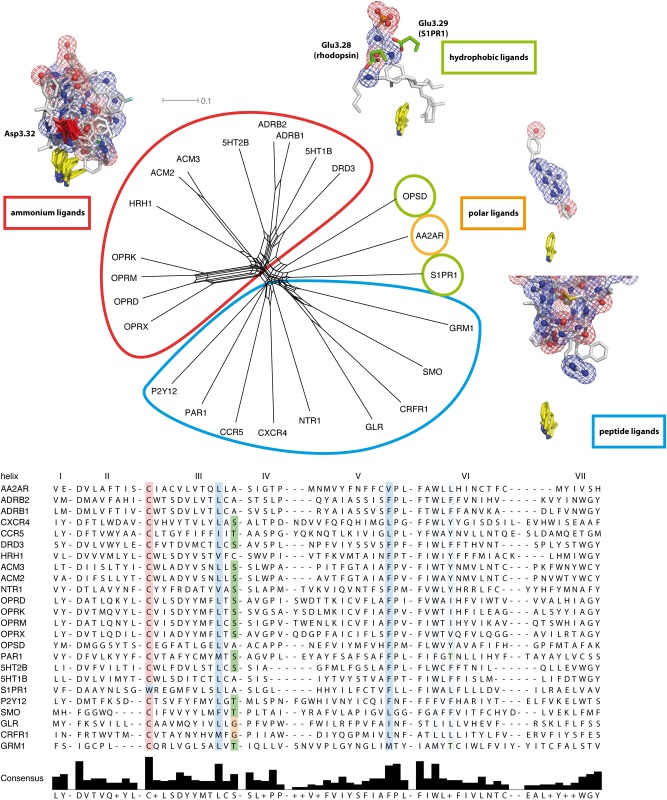
Fig 5. NeighborNet analysis of GPCR ligand binding sites.
Top: uncorrected P distance based NeighborNet of residues forming the ligand binding sites in GPCR crystal structures. Ligands and characteristic residues in sticks, their characteristic contact-forming polar oxygen/nitrogen atoms as spheres and mesh. Trp6.48 in yellow displayed as visual point of reference. The network analysis reveals four dominant categories of ligand binding cavities: peptide ligand receptors (cyan), hydrophobic ligand receptors (green), containing opsins and sphingosine receptors, polar ligand receptors (orange), containing adenosine receptors; and ammonium ligand receptors (red), containing muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, biogenic amine receptors, and opioid receptors. Hydrophobic ligand receptors share a glutamate at the similar positions 3.28 or 3.29. Surprisingly, opioid receptors are found in a group together with biogenic amine receptors, but not with peptide ligand receptors. They share the major contact residue Asp3.32 with acetylcholine and biogenic amine receptors. Bottom: Sequence alignment of amino acids forming small molecule binding sites in analyzed GPCR crystal structures.