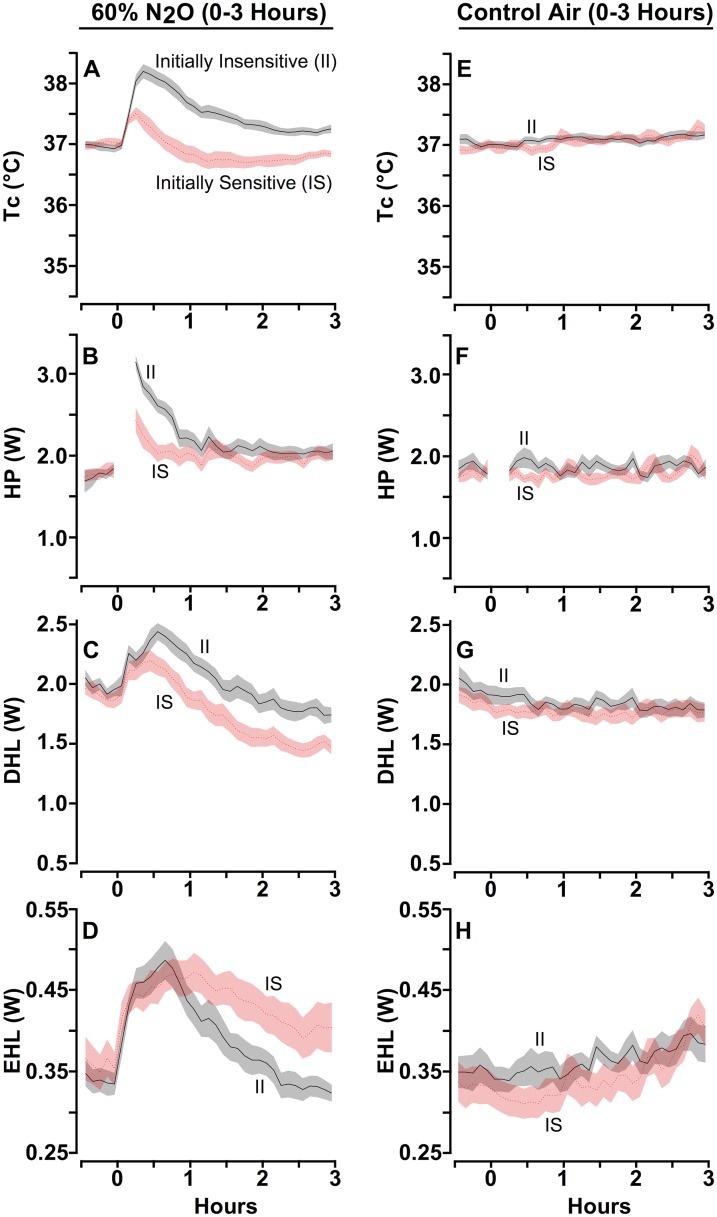
Fig 4. Final Calorimetric Assessment during a 60% N2O Administration for Initially Sensitive and Initially Insensitive Rats.
A calorimetry retest conducted after the self-administration phase revealed that the IS and II groups both became frankly hyperthermic with the onset of 60% N2O administration but the magnitude was markedly greater and more persistent in the N2O self administration-prone II rats (A) due primarily to a greater HP response (B). The increases in DHL (C) and EHL (D) likely reflect a durable pharmacological effect of N2O in addition to the effect of increased body heat content to promote heat loss. The II and IS groups did not differ during the control gas session (E, F, G, H).