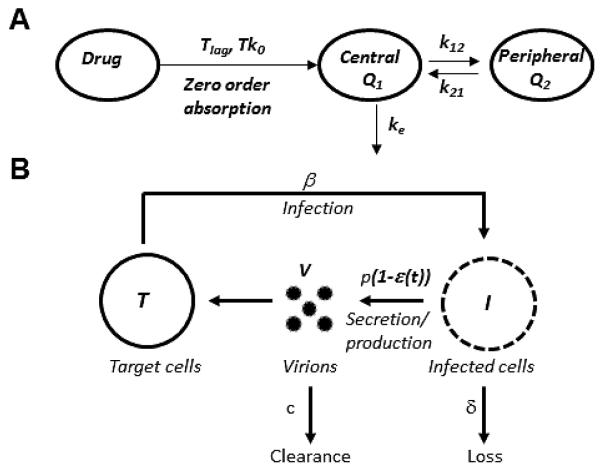
Figure 1. Combined PK/VK model used to describe viral kinetics during danoprevir monotherapy.
(A) Schematic of the two-compartment PK model following zero-order absorption of danoprevir. Danoprevir is absorbed, after a lag time Tlag into the central compartment/blood plasma (Q1) following a zero order absorption law with rate constant Tk0. Danoprevir is eliminated from the central compartment via a first order elimination process with rate constant ke, and moves in to and out of the second compartment (Q2) with forward and backward rate constant k12 and k21, respectively. (B) Schematic representation of the VK model. Danoprevir inside infected cells, I, is considered to partially block viral RNA production with a time varying effectiveness, ε(t), which depends on the danoprevir concentration. Target cells, T, are infected by virus, V, with rate constant β to produce infected cells, I. Infected cells, I, are lost with rate constant δ and virus, V, is cleared from the circulation with rate constant c. In the absence of drug infected cells produce virus with rate p per infected cell.