Table 2.
Mono-substituted benzylic substituents at the 1-position and their effect on OX antagonism
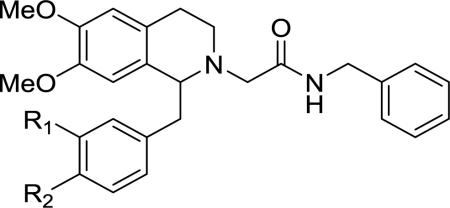
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | R1 | R2 | Ke (OX1, nM)b | Ke (OX2, nM)c | OX2/OX1 |
| 11 | OMe | OMe | 199± 47 | >10,000 | >50.3 |
| 41 | O-Isopropyl | H | 1470± 70 | >10,000 | >6.8 |
| 42 | NO2 | H | >10,000 | 1200± 160 | <0.12 |
| 43 | NH2 | H | 1310± 90 | a | |
| 44 | NMe2 | H | 75.3± 1.3 | 660±160 | 8.8 |
| 45 | H | O-n-Propyl | 370± 50 | >10,000 | >27 |
| 46 | H | O-Isopropyl | 489± 68 | >10,000 | >20 |
| 47 | H | NH2 | >10,000d | a | |
| 48 | H | NMe2 | 253± 85 | >10,000 | >40 |
| 49 | H | NHAc | >10,000d | a | |
| 50 | H | NHCONH-n-hexyl | >10,000d | a | |
| 51 | H | Isopropyl | 85± 21 | >10,000 | >118 |
< 35% inhibition at 10 μM
Values are the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments performed in duplicate
Values are the mean ± SEM of at least two independent experiments in performed duplicate; for compounds with Ke < 100 nM at OX1 at least three independent experiments in duplicate were performed.
Values are the mean ± SEM of two independent experiments performed in duplicate.
