Fig. 1.
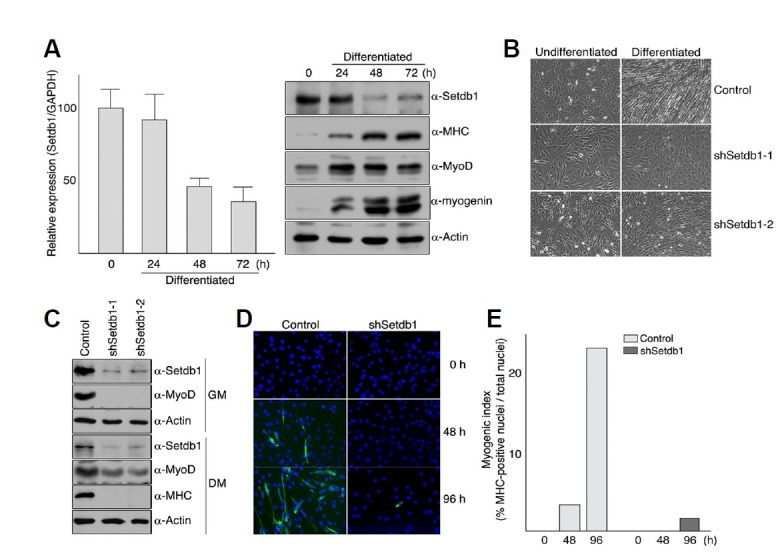
Inhibition of myogenic differentiation by Setdb1 depletion. (A) levels of Setdb1 decrease during C2C12 myoblast differentiation. C2C12 myoblast cells were grown to confluency in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and differentiation was induced by serum withdrawal. Cells were harvested at the indicated time points and total RNAs or total protein extracts were prepared as described in “Materials and Methods”. RNA was analyzed by quantitative real-time RT-PCR using primers specific for Setdb1 and GAPDH. Relative expression of Setdb1 was determined using the standard curve method and then normalized to GAPDH. Error bars indicate standard deviation (left). Proteins were resolved on 7.5% (for Setdb1 and MHC) or 12% (for MyoD, myogenin, and Actin) SDS-PAGE and detected with antibodies against indicated proteins (right). (B-E) C2C12 myoblast cells with Setdb1 shRNA displayed severely delayed differentiation under serum-deprived conditions. C2C12 myoblast cells stably expressing control vector (pLKO.1) or Setdb1 shRNA were maintained in DMEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum and differentiation was initiated as described in Materials and methods. After 72 h, differentiation was assessed by the appearance of myotubes using photomicrograph (B), expression of MHC as well as endogenous MyoD using Western blot analysis (C), and number of MHC-positive nuclei per 103 cells using immunofluorescence (D, E).
