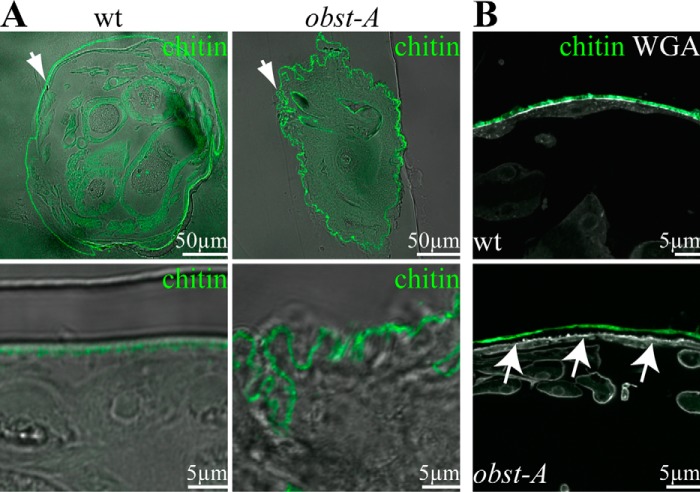
FIGURE 1.
Obst-A is required for larval body shape control and epidermal cuticle integrity. A and B, confocal and bright field (bf) images show larval cross-sections. Chitin is visualized by Cbp (green) and WGA (gray, B) marks on the apical cell surfaces. A, in 97% (n = 27) of wild type first instar larvae the cuticle (green) is evenly attached to the epidermal cells. In 54% (n = 24) of obst-A mutant first instar larvae, the epidermal cuticle is wrinkled, and the body circumference is increased. Images are generated by confocal sections and bright field microscopy. The upper panels show cross-sections of the larvae (arrows point to the epidermis), and the lower panels show magnifications of the epidermal cuticle. B, in 97% (n = 27) of wild type larvae, the cuticle is tightly attached to epidermal cells and marked by WGA. In 29% (n = 24) of obst-A mutant larvae, the cuticle was detached (arrows) from the underlying epidermal cells (arrows). Scale bars represent 50 or 5 μm, respectively.