FIGURE 5.
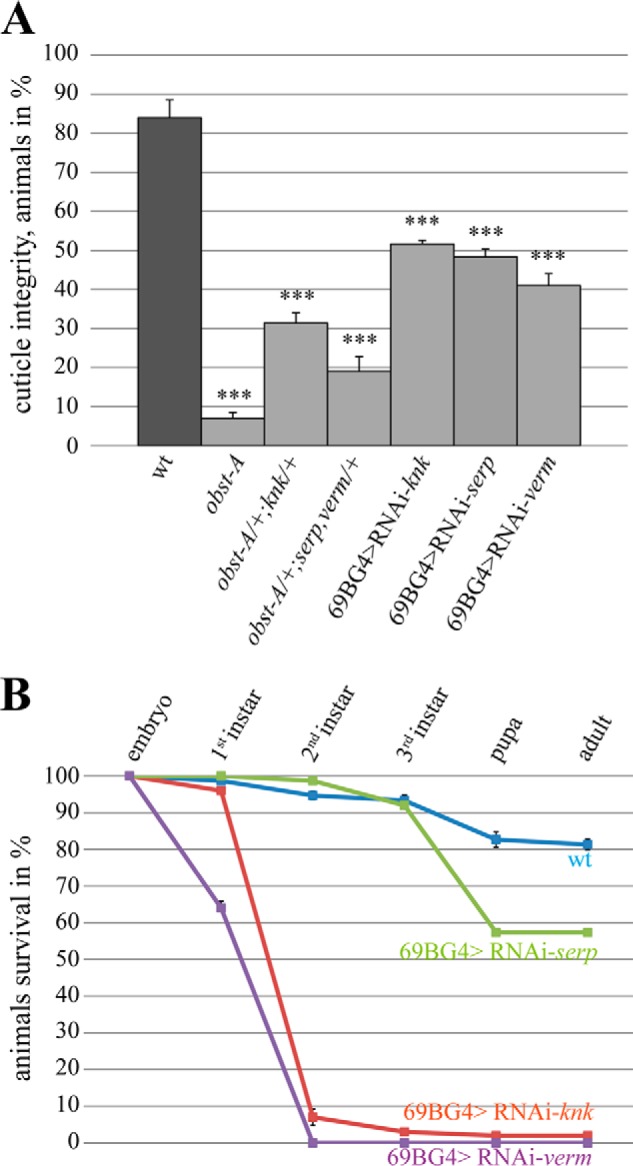
knk, serp, and verm are required for epidermal cuticle integrity and larval survival. A, cuticle integrity test was performed by pricking first instar larvae according to Petkau et al. (19). 84% of wild type larvae (n = 94) survived pricking without severe wounding, whereas 93% of obst-A mutant larvae (n = 46) showed severe epidermal disruption, which caused organ spill and immediate lethality. A large number of transheterozygous larvae (obst-A/+,knk/+ (n = 60) and obst-A/+,serp,verm/+ (n = 65)) showed obst-A mutant-like cuticle integrity defects. Similar cuticle integrity defects were observed in knk (48%, n = 103), serp (52%, n = 66), and verm (59%, n = 58) knockdown larvae. The p values are represented by asterisks: *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; and ***, p < 0.001. B, survival tests revealed larval lethality for knk, serp, and verm knockdown mutants but not for wild type. The test was repeated four times with n = 25 larvae of each genotype. Less than 1% of verm knockdown larvae reach the third instar stage. The error bars represent the standard error, and p values are represented by asterisks. Note that the knockdown efficiency for all RNAi lines as determined by qRT-PCR was ∼90% (data not shown).
