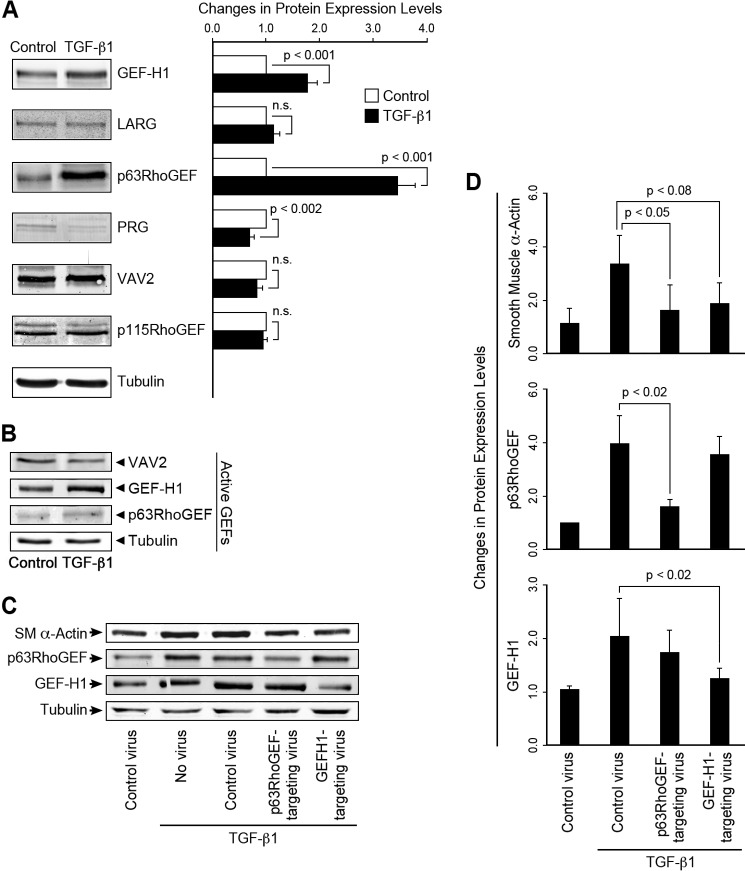
FIGURE 3.
TGF-β1-induced EMT increased the expression and activity of p63RhoGEF and GEF-H1, but not VAV2 and EMT, and partial silencing of p63RhoGEF and GEF-H1 expression suppressed EMT as indicated by a decrease in SMA expression. A, protein expression, detected by Western blotting, of p63RhoGEF, GEF-H1, but not LARG, VAV2, or p115RhoGEF, significantly increased with TGF-β1 treatment, n = 12–16. Cells were stimulated with TGF-β1 (250 pm) for 72 h. The protein level of PDZRhoGEF (PRG) was decreased. n.s., not significant. B, GEF-H1, but not VAV2 activity, measured with a RhoG17A mutant to capture active RhoGEFs increased with TGF-β1-induced EMT; n = 3. A trend in increase of p63RhoGEF activity did not reach significance. RhoGEF protein levels were normalized to tubulin. Data are presented as the means ± S.E. C and D, lentiviral shRNAs to p63RhoGEF and GEF-H1 and empty vectors (controls) were introduced into mouse embryonic epicardial cells, and the extent of GEF suppression and SMA protein expression was measured by Western blotting 48 h after stimulation with TGF-β1, n = 3. Expression of SMA was significantly decreased with suppression of p63RhoGEF or GEF-H1.