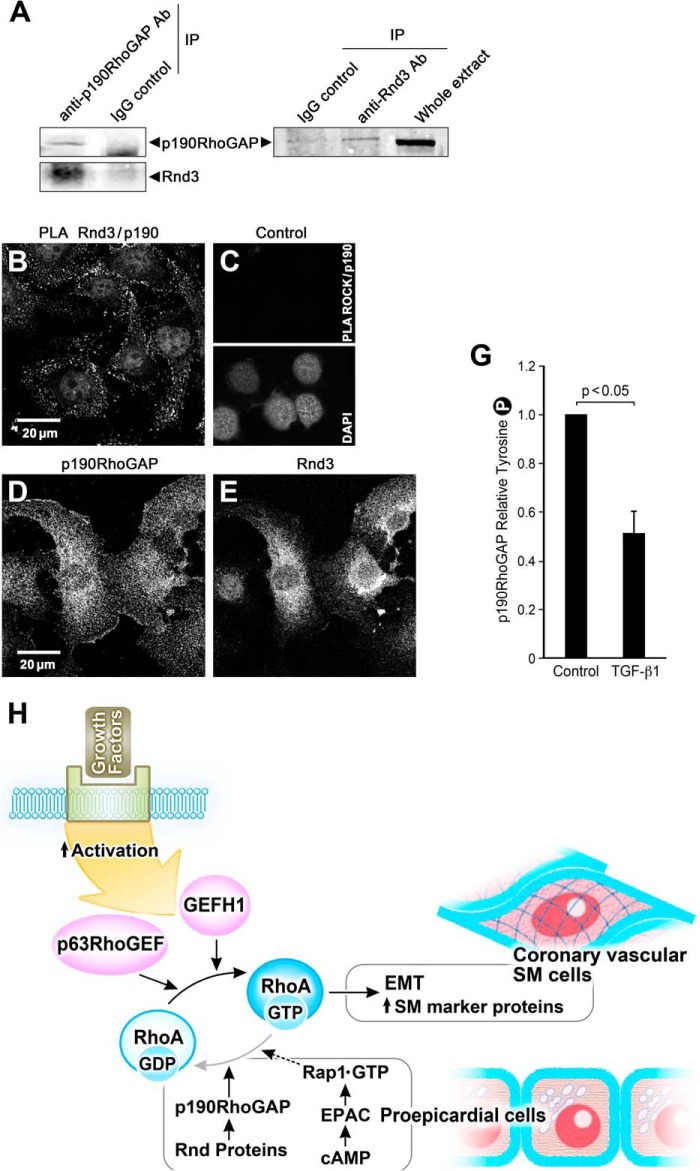
FIGURE 7.
Rnd3 associates with p190RhoGAP in epicardial cells in the epithelial state; overall signaling scheme. A, anti-p190RhoGAP antibody, but not a nonspecific mouse IgG antibody, coimmunoprecipitated (IP) endogenous p190RhoGAP and Rnd 3. Anti-Rnd3 antibody, but not a nonspecific IgG, coimmunoprecipitated endogenous Rnd3 and p190RhoGAP. B, PLA demonstrating a proximity of <40 nm of Rnd3 and p190RhoGAP in EMCs as evidenced by each bright dot. C, control for PLA illustrating that under the same conditions no signal was observed for p190RhoGAP antibody and ROCK antibody. The presence of cells is indicated by the nuclear stain DAP1. D and E, control panels for the PLA assay showing the immunofluorescence of p190 RhoGAP and Rnd3 antibodies in these cells. G, p190RhoGAP activity, as indicated by Tyr-1105 phosphorylation, significantly decreases in the presence of 250 pm TGF-β1 (36 h) in EECs; n = 8. H, scheme of signaling pathways contributing to the maintenance of the proepicardial progenitor phenotype. EMT initiated by growth factors leads to activation of p63RhoGEF and GEF-H1 to exchange GTP for GDP and activate RhoA to stimulate the transcription of SM marker proteins such as SMA, SM myosin, and SM22 and transformation of the proepicardial cells into coronary vascular SM cells. RhoA activity is suppressed and kept in check in the proepicardial cells by the increased activity of p190RhoGAP and Rnd proteins as well as through signaling from cAMP to Epac, the GTP exchange factor for the small GTPase, Rap1, to further down-regulate RhoA activity.