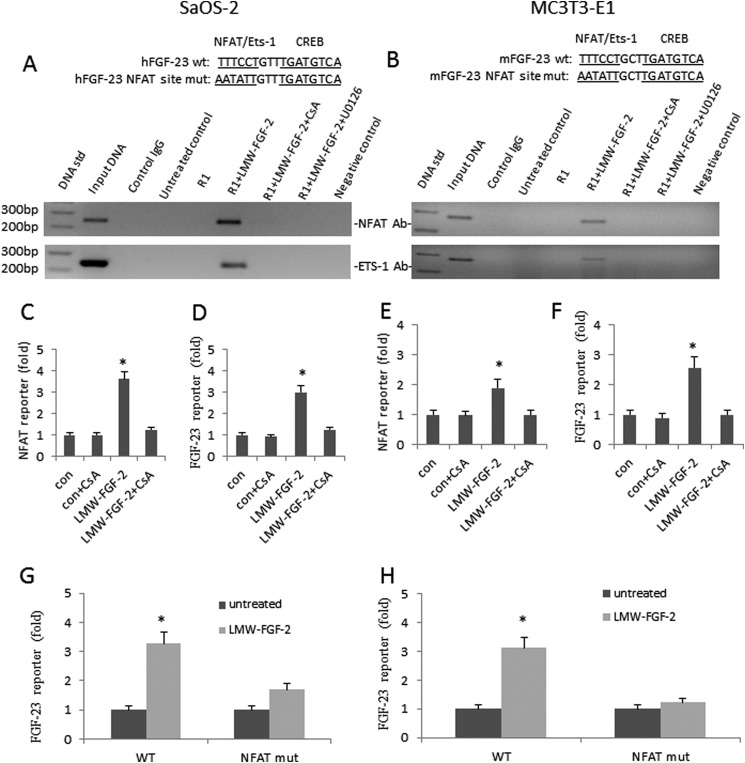
FIGURE 2.
LMW-FGF-2 up-regulates FGF-23 gene transcription via NFAT and MAPK pathways. A and B, LMW-FGF-2 enhanced NFAT and Ets-1 binding to the endogenous FGF-23 promoter as determined by CHIP assay using NFAT or Ets-1 antibody. First lane, 100-bp DNA standard; second lane, input ChIP DNA; third lane, nonspecific IgG; fourth lane, untreated control cells; fifth lane, FGFR1 co-transfected cells; sixth lane, FGFR1 co-transfected cells treated with LMW-FGF-2 (50 ng/ml) for 24 h; seventh lane, FGFR1 co-transfected cells treated with LMW-FGF-2 (50 ng/ml) in the presence of CsA (1 μm) for 24 h; eighth lane, FGFR1 co-transfected cells treated with LMW-FGF-2 (50 ng/ml) in the presence of U0126 (10 μm) for 24 h; and ninth lane, negative control. C and E, LMW-FGF-2 stimulates NFAT activity in both SaOS-2 and MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts. Cyclosporine A (1 μm) blocks the effect of LMW-FGF-2 on NFAT reporter gene expression. D and F, LMW-FGF-2 stimulates FGF-23 promoter activity in both SaOS-2 and MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts. Cyclosporine A (1 μm) blocks the effect of LMW-FGF-2 on FGF-23 reporter gene expression. G and H, LMW-FGF-2 stimulates both human and mouse FGF-23 promoter activities. NFAT site mutation blocks LMW-FGF-2 effect. Data are expressed as the mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05 versus control vector group.