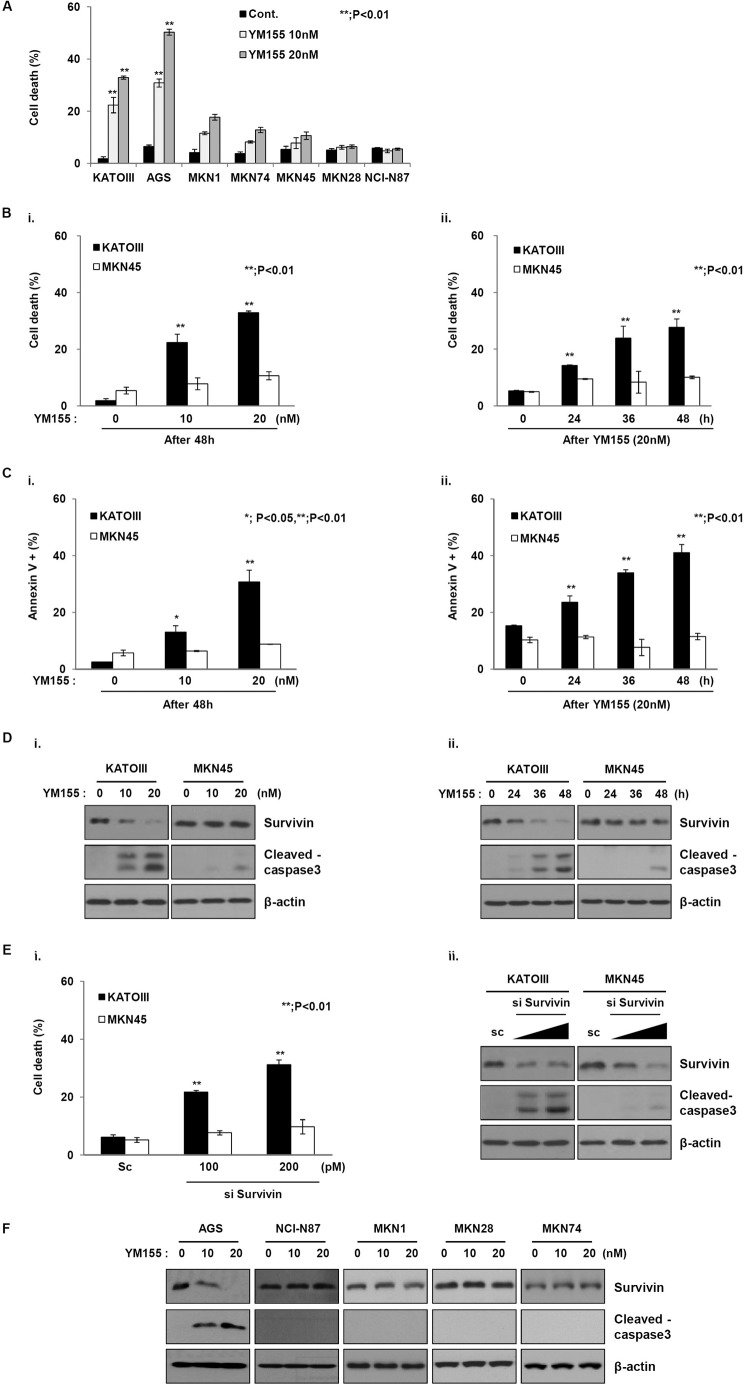
FIGURE 1.
YM155 differentially induces cell death in gastric cancer cells. A, mutiple gastric cancer cells were treated with YM155 for 48 h at the indicated doses. Cell death was evaluated by a trypan blue exclusion assay. B, (i) KATOIII and MKN45 cells were treated with YM155 at the indicated doses for 48 h, or (ii) YM155 (20 nm) at the indicated times. Cell death rate was determined using the trypan blue exclusion method. The error bars represent the mean ± S.D. of three experiments in triplicate. **, p < 0.01. C, (i) KATOIII and MKN45 cells were treated with YM155 at the indicated doses for 48 h, or (ii) YM155 (20 nm) at the indicated times. Cell death was analyzed by annexin V staining using flow cytometry. D, (i) KATOIII and MKN45 cells were treated with YM155 at 10 and 20 nm for 48 h, and the cell lysates were analyzed using Western blotting with anti-survivin and anti-cleaved caspase-3 antibodies; β-actin was used as a loading control. (ii) YM155 (20 nm) cells treated for 48 h were used for Western blotting using anti-survivin, anti-cleaved caspase-3, and the loading control β-actin. E, the cells were transfected with scramble or survivin siRNA for 48 h. (i) Cell death was determined using the trypan blue exclusion method. The graph represents the mean ± S.D. of three separate experiments in triplicate; *, p < 0.01. (ii) The cell lysates were used for Western blot analysis to determine the expressions of survivin, cleaved caspase-3, and β-actin. F, cells were treated with YM155 for 48 h at the indicated doses and then analyzed by Western blot using anti-survivin and anti-cleaved caspase-3. β-Actin was used as a loading control.