Figure 5.
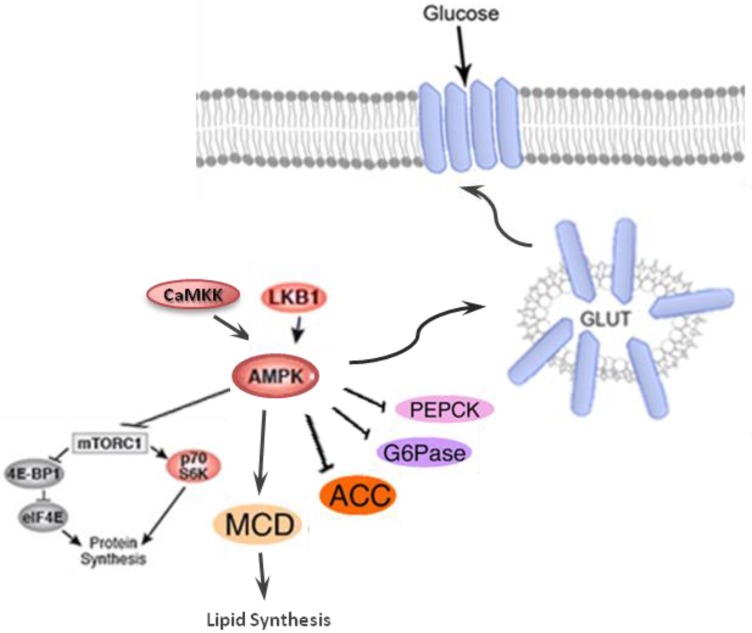
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) which is the central energy leads to decreases hepatic glucose production via inhibiting the activation of gluconeogenic enzymes phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) and glucose 6-phosphatase (G6Pase); induction of glucose uptake through inducing GLUT-4 and GLUT-1 and stimulation of lipid metabolism via declining malonyl CoA levels by inhibiting acetyl CoA carboxylate (ACC) and activation of malonyl CoA decarboxylase.