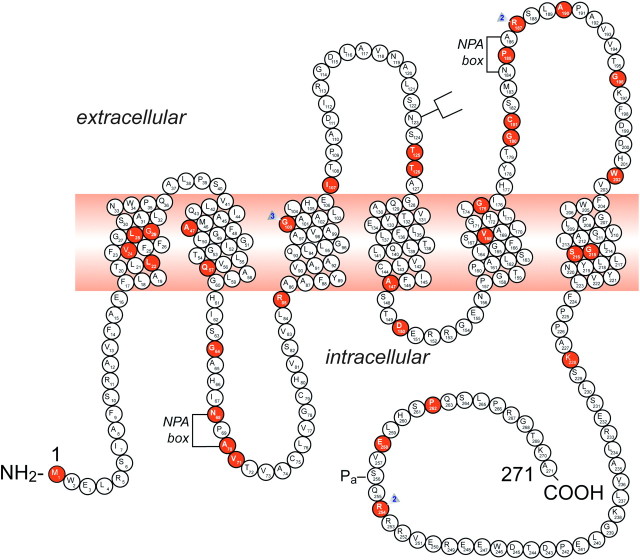
Fig. 3.
A representation of the AQP2 protein and identification of 46 putative disease-causing AQP2 mutations. A monomer is represented with six transmembrane helices. The location of the PKA phosphorylation site (Pa) is indicated. The extracellular, transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains are defined according to Deen et al. [17]. Solid symbols indicate the location of the mutations (for references, view Table 1): M1I; L22V; V24A; L28P; G29S; A47V; Q57P; G64R; N68S; A70D; V71M; R85X; G100X; G100V; G100R; I107D; 369delC; T125M; T126M; A147T; D150E; V168M; G175R; G180S; C181W; P185A; R187C; R187H; A190T; G196D; W202C; G215C; S216P; S216F; K228E; R254Q; R254L; E258K and P262L. GenBank accession numbers—AQP2: AF147092, Exon 1; AF147093, Exons 2 through 4. NPA motifs and the N-glycosylation site are also indicated.