Fig. 1.
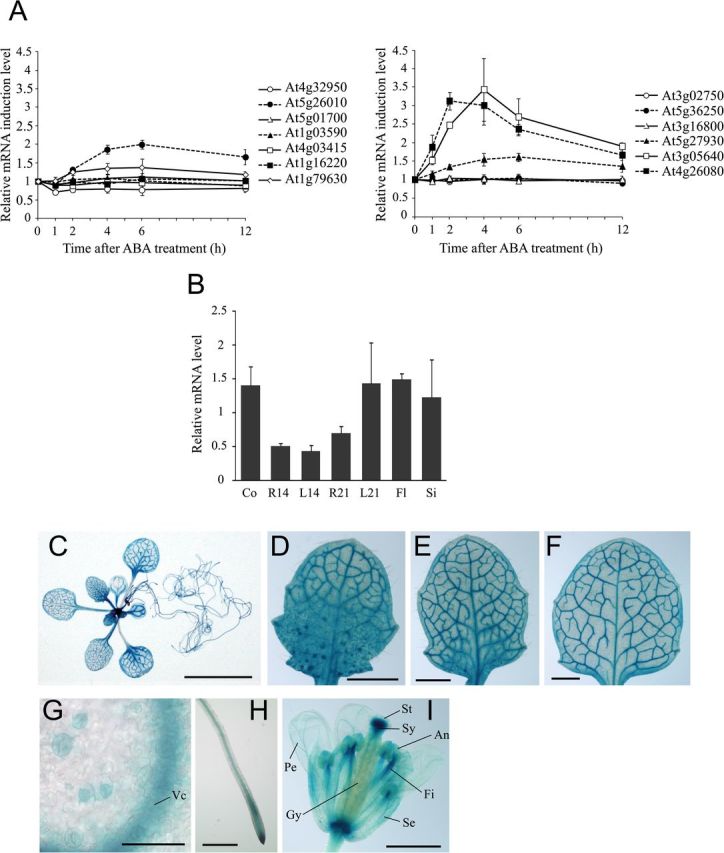
Spatial, temporal, and ABA-mediated regulation of AtPP2CF1 expression. Arabidopsis plants were germinated aseptically on MS medium with gellan gum. At 21 d after germination, seedlings were transferred to soil. (A) Time course of the induction of subfamily E PP2C mRNA expression in aerial parts of wild-type Arabidopsis plants in response to exogenous ABA. Two-week-old seedlings were sprayed with 10 μM ABA or 0.1% DMSO (mock control). Total RNA from aerial parts was isolated at the indicated time points after ABA or mock treatment and subjected to RT-qPCR. The expression ratios of individual subfamily E PP2C genes to UBC9 were calculated for each time point and treatment (raw data are shown in Supplementary Fig. S3), and induction of each PP2C mRNA after ABA treatment was calculated by dividing the expression after ABA treatment by the expression after mock treatment at each time point. Values represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. (B) Expression of AtPP2CF1 transcripts. Total RNA from different tissues of wild-type Arabidopsis plants was isolated and subjected to RT-qPCR. The expression ratios of AtPP2CF1 to UBC9 were calculated for each sample. Values represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Co, 7-d-old cotyledons; R14, 14-d-old roots; L14, 14-d-old first and second rosette leaves; R21, 21-d-old roots; L21, 21-d-old first to fourth rosette leaves; Fl, flowers; Si, siliques. (C–I) Histochemical analysis of GUS activity in Arabidopsis pAtPP2CF1:GUS transgenic plants. (C) A 21-d-old seedling. (D–F) A developmental series of rosette leaves ranging from young (D) to old (F) within a 21-d-old transgenic seedling. (G) Guard cells of young leaves. (H) Roots. (I) Flowers. Vc, vascular cylinder; An, anther; Fi, filament, Gy, gynoecium; Pe, petal; Se, sepal; St, stigma; Sy, style. Scale bars: 10mm (C); 1mm (D–F, I); 500 μm (H); 50 μm (G).
