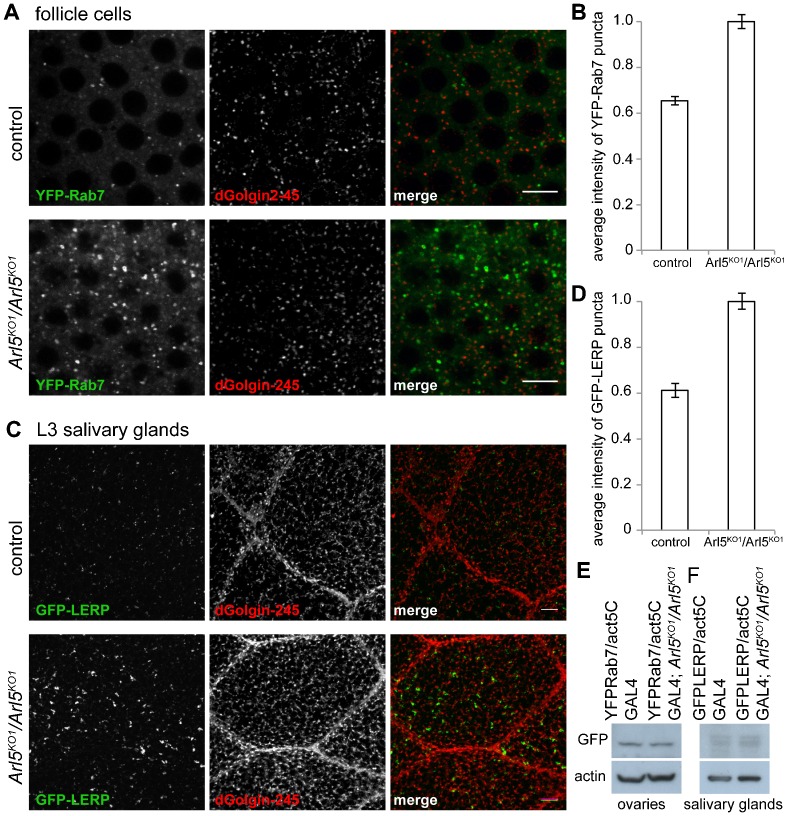
Fig. 5. Loss of Arl5 leads to the accumulation of swollen endosomal compartments.
(A) Cross-section view of epithelial follicle cells of control (w1118) and Arl5KO1 mutant (Arl5KO1/Arl5KO1) shows that the loss of Arl5 results in the accumulation of enlarged late endosomal and lysosomal structures, marked by the exogenously expressed marker YFP-Rab7 (green). The trans-Golgi marker dGolgin-245 remains largely unaltered between mutant and control follicle cells. (B) Quantification of the extent of accumulation of YFP-Rab7-containing structures. A single image such as those in (A) was obtained from each of 13 flies for each stock, and a mean determined of average intensity of the cytoplasmic puncta in each image. Error bars show standard error of mean. The average fluorescence relative to that of cytoplasm being approximately 1.5× higher in the Arl5KO1 homozygous mutant. (C) Confocal micrographs of L3 larval salivary glands from control (w1118) and Arl5KO1 mutant (Arl5KO1/Arl5KO1), expressing a GFP-tagged form of the Drosophila receptor of precursor of lysosomal hydrolases (LERP), revealed that absence of Arl5 leads to the enlargement of structures positive for GFP-LERP (green), which only localized moderately with dGolgin-245 (red), both in control and in the Arl5KO1 mutant. (D) Quantification of the extent of accumulation of GFP-LERP- containing structures. A single image such as those in (C) was obtained from each of 9 flies for each stock, and a mean determined of the average intensity of the cytoplasmic puncta in each image. Error bars show standard error of mean. The average fluorescence of GFP-LERP positive structures versus that of the cytoplasm is 1.6× higher in the Arl5KO1 mutant than in control L3 salivary gland cells, suggesting its altered retrograde traffic from endosomes to the TGN. Scale bars are 10 µm. (E) Anti-GFP immunoblots of extracts from ovaries of flies that express YFP-Rab7 and either have, or lack, Arl5. (F) Anti-GFP immunoblots of extracts from salivary glands of flies that express GFP-LERP and either have, or lack, Arl5.