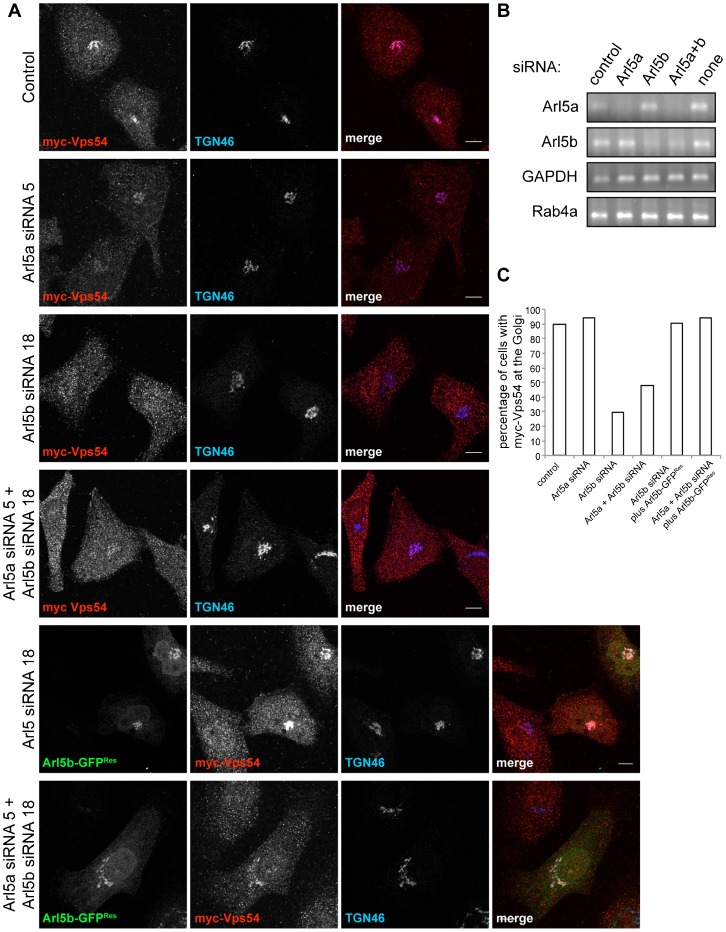
Fig. 6. Arl5b is required for the recruitment of Vps54 to the TGN.
(A) Confocal micrographs of HeLa cells expressing myc-Vps54 (red) and depleted of mock (control) or the indicated proteins with siRNAs and stained for TGN46 (blue). Knockdown of Arl5b or of Arl5a and Arl5b, simultaneously resulted in the striking redistribution of myc-Vps54 from the TGN to the cytoplasm. Expression of a siRNA-resistant form of Arl5b-GFP (Arl5b-GFPRes) was sufficient to rescue the mislocalization of myc-Vps54 upon depletion of either Arl5b or of Arl5a and Arl5b. Scale bars are 10 µm. (B) RT-PCR from HeLa cells silenced for the indicated proteins with siRNAs showed the efficient depletion of the corresponding mRNAs. Amplification of the housekeeping gene GAPDH and of Rab4a was used as a control for the total amount of mRNA across all samples. (C) Quantification of the effect of depletion of the proteins indicated in (A) on the localization of myc-Vps54. Transfected cells were examined for detectable myc-Vps54 on the Golgi (n = 29, 28, 47, 52, 32, 18 respectively). Strikingly, myc-Vps54 was redistributed from the TGN to the cytoplasm in 70% of cells silenced for Arl5b and in 52% of cells depleted for Arl5a and Arl5b. Expression of a siRNA-resistant form of Arl5b-GFP in cells depleted for Arl5b alone or for Arl5a and Arl5b increased the number of cells with myc-Vps54 at the TGN to levels comparable to mock silenced cells (control).