Figure 1.
KD of L3MBTL1 Primes the Hematopoietic Potential of iPSCs
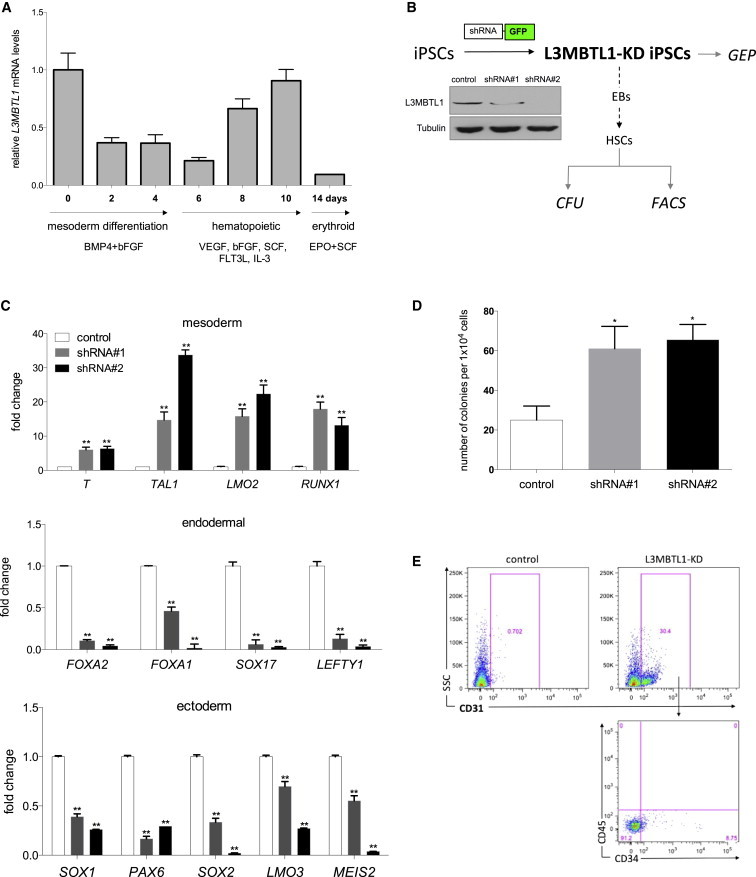
(A) Endogenous L3MBTL1 expression was assessed in iPSCs at different time points during the mesodermal, hematopoietic, and erythroid differentiation using quantitative real-time PCR. The data represent the mean ± SD of the three independent experiments.
(B) Strategy diagram. L3MBTL1 expression is efficiently knocked down as assessed by western blot assay in undifferentiated iPSCs. Tubulin served as the loading control.
(C) KD of L3MBTL1 increases the expression of mesodermal-specific transcription factors while it decreases expression of key markers of endodermal and ectodermal lineages, as shown in L3MBTL1-KD undifferentiated iPSCs by qPCR compared to controls. Data indicate the relative expression level of the gene of interest, normalized by GAPDH. The reported fold changes have been calculated by ΔΔCt analysis versus control cells. The data represent the mean ± SD of the three independent experiments. ∗∗p < 0.01 by Student’s t test.
(D) KD of L3MBTL1 increases CFU capacity of iPSC-derived HSCs. Cells from day 10 hEBs were plated in methylcellulose and colonies were scored after 15 days. The data represent the mean ± SD of the three independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05 by Student’s t test.
(E) KD of L3MBTL1 promotes the emergence of early hemogenic precursor cells. EBs were harvested at day 10, prior to CD45 emergence, and analyzed by flow cytometry for CD31 and CD34 expression.
Refer to Figure S1 for the characterization of the iPSC line generated from cord blood CD34+ cells.
