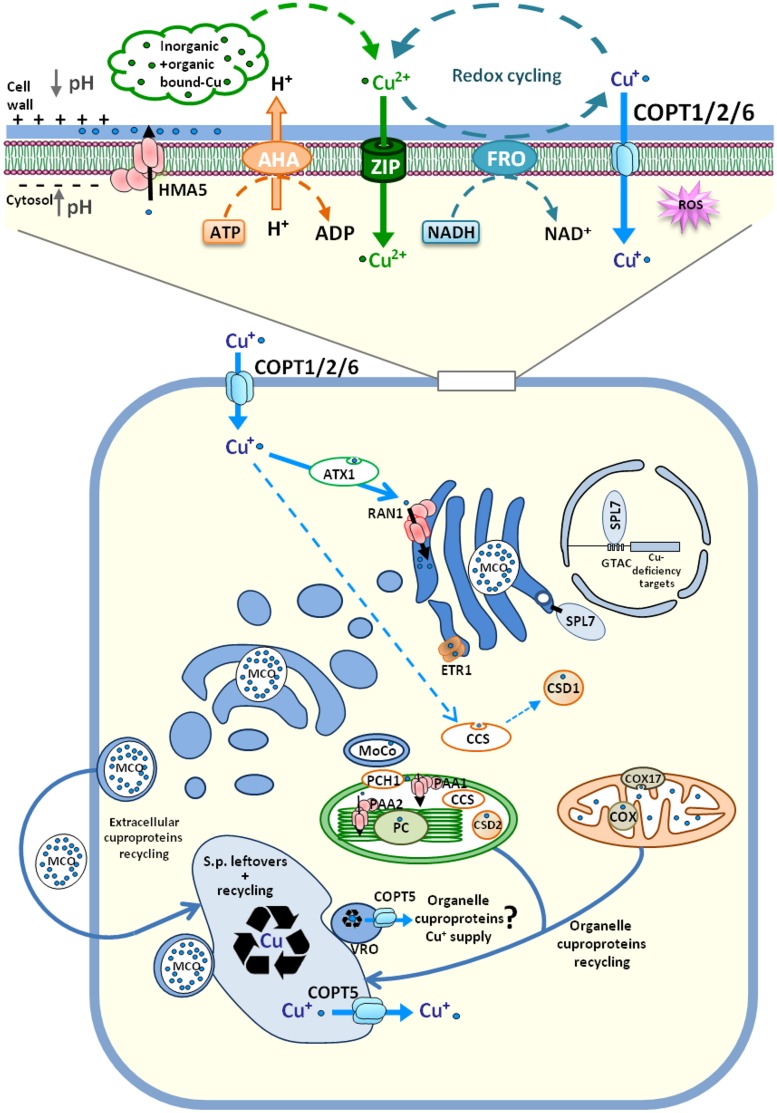
FIGURE 1.
Overview of Arabidopsis thaliana cellular Cu homeostasis. Cu+ uptake through plasma membrane transporters COPT1/COPT2/COPT6 depends on the activity of AHA H+-ATPase and FRO cuproreductases. COPT-mediated Cu+ transport is coupled to metallochaperones transfer and its delivery to targets. Cuprochaperone CCS provides Cu+ to cytosolic superoxide dismutase CSD1. ATX1 transfers Cu+ to P-type ATPase RAN1, located at the ER, where Cu+ is probably acquired by cuproproteins, such as multicopper oxidases (MCOs), the ethylene receptor (ETR1), and the molybdenum cofactor (MoCo). The Cu resulting from recycling and from the secretory pathway leftovers converges into the vacuole or into vacuolar-related organelles (VROs). The Cu+ supply to chloroplasts and mitochondria can take place from the lumen through the COPT5 efflux function. See the main text for details. The direction of Cu+ traffic is indicated by arrows and Cu content is indicated by different intensities of blue.