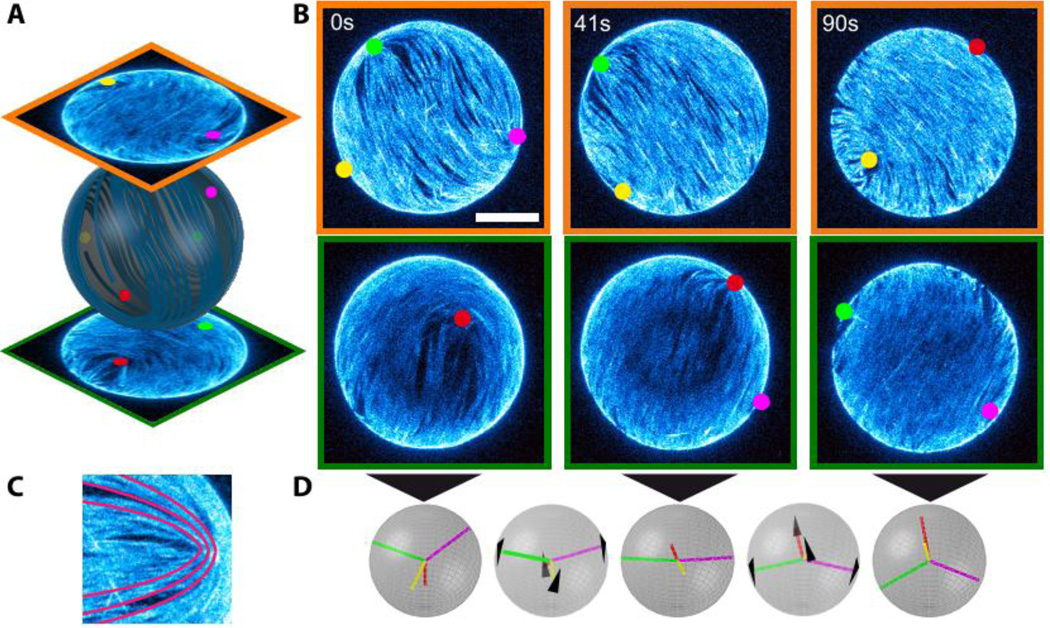
Figure 1. Defects dynamics of an active nematic film on the surface of a spherical vesicle.
(A) Hemisphere projection of a 3D confocal stack of a nematic vesicle identifying the position of four +½ disclination defects. (B) Time series of hemisphere projections over a single period of oscillation in which the four defects switch from tetrahedral (t=0s) through planar (t=41s) and back to tetrahedral (t=90s) configurations. Bar is 20µm. (C) Comet-like +½ disclination defect with schematic of the orientation of the nematic director (red lines). (D) Schematic of the defect configurations at the timepoints of (B) and intermediate times (t=24s, t=65s). The black arrows indicate the direction of defect motion.