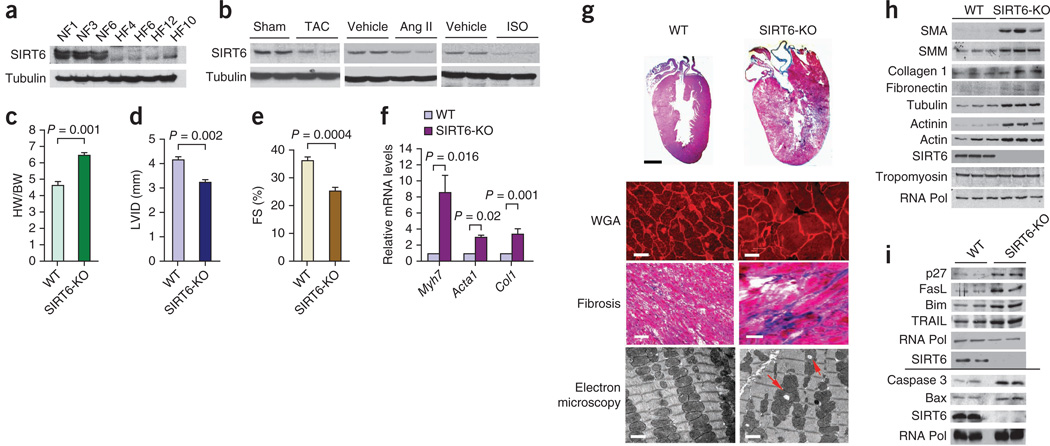
Figure 1.
SIRT6 deficiency causes cardiac hypertrophy and degenerative changes in the heart. (a) Western blot showing SIRT6 expression in human heart samples from representative normal control hearts (NF1, NF3, NF6; n = 8) and failing hearts (HF4, HF6, HF12, HF10; n = 24) (Supplementary Table 1). Tubulin was used as a loading control. (b) Representative western blots showing SIRT6 expression in heart samples from mice subjected to TAC or chronic infusion of ISO or angiotensin II (Ang II). n = 8 mice per group. (c) HW/BW ratio of wild-type (WT) and SIRT6 knockout (SIRT6-KO) mice at 8 weeks of age. n = 13 mice per group. Data are presented as means ± s.d. (d,e) Left ventricular internal diameter (LVID; n = 7 mice per group) and fractional shortening (FS; n = 10 mice per group) of WT and SIRT6 knockout mice at 8 weeks of age as determined by echocardiography. Data are presented as means ± s.d. (f) mRNA levels of the indicated genes in heart samples of WT and SIRT6 knockout mice. n = 6 mice per group. Data are presented as the mean ± s.d. For c–f, Student’s t test was used to calculate the P values. (g) Whole-heart sections stained with H&E showing concentric hypertrophy in SIRT6 knockout hearts (top row; scale bar, 2 mm); left ventricular muscle sections stained with wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) to demarcate cell boundaries (second row; scale bars, 10 µm) or Masson’s trichrome to detect fibrosis (third row; scale bars, 40 µm); and electron micrographs showing vacuolization (red arrows) and degeneration of mitochondria in SIRT6 knockout hearts (bottom row; scale bars, 1 µm). (h,i) Representative western blots showing the expression of the indicated fibrosis markers, cytoskeletal proteins and apoptotic markers in WT and SIRT6 knockout hearts. n = 6 per group. The line between the blots indicates two different gels. RNA Pol, RNA polymerase; SMA, α-smooth muscle actin; SMM, smooth muscle myosin.