3.
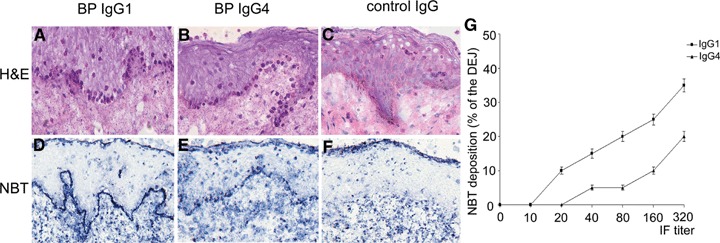
IgG4 autoantibodies recruit and activate leucocytes. Sections of human skin were incubated with IgG1 and IgG4 autoantibodies from a BP patient, as well as with IgG from a healthy control. Subsequent addition of leucocytes from healthy donors leads to leucocyte attachment at the dermal–epidermal junction in sections treated with patient's IgG1 (A) and IgG4 autoantibodies (B), but not in sections incubated with control IgG (C). Activation of leucocytes, as revealed by the reduction of nitro blue tetrazolium (NBT) to formazan (dark precipitates), is induced by purified IgG1 (D) and IgG4 autoantibodies (E), but not by control IgG (F) (all magnifications, ×400). (G) Cryosections of human skin were treated with IgG1 (n = 3) and IgG4 (n = 5) antibodies (four sections/antibody preparation). Subsequently, leucocytes from healthy donors were incubated for 90 min with the cryosections. Deposition of formazan is represented as means ± SEM of the percent of the total length of the dermal–epidermal junction (DEJ) for each section.
