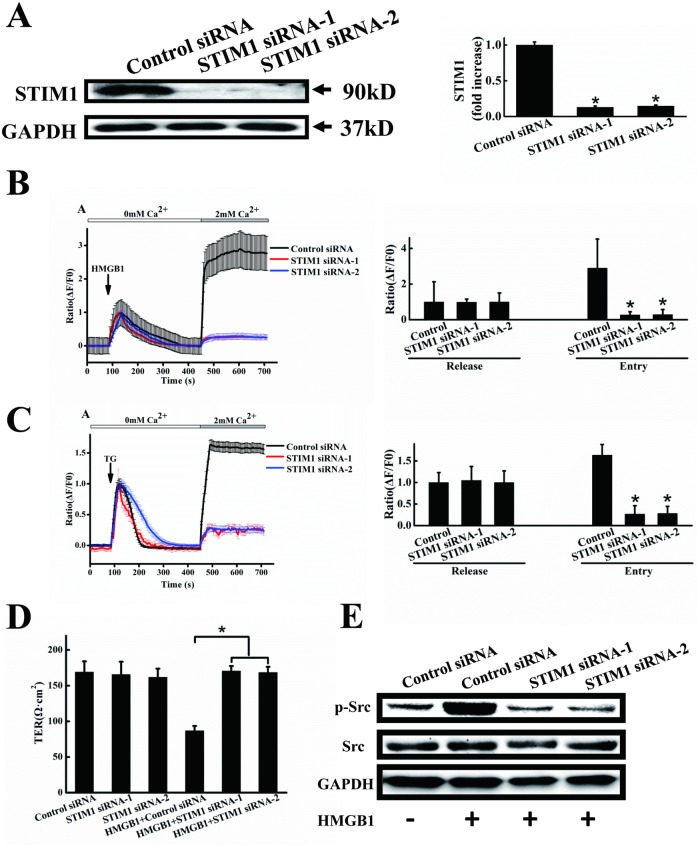
Fig 6. STIM1 knockdown decreases Ca2+ influx, HMGB1-induced permeability and Src phosphorylation.
A. STIM1 protein expression after RNA inference. EA.hy926 cells were transfected for 48 h with STIM1 siRNA-1, siRNA-2 or control (scrambled) siRNA. Cells were harvested and total protein was extracted and subjected to western blotting with anti-STIM1 antibodies, with anti-GAPDH antibodies as a loading control. STIM1 expression was quantified and analyzed statistically based on three independent experiments. Transfected cells were also stimulated with 200 ng/ml HMGB1 (B) or 1 μM TG (C), followed by the addition of 2 mM CaCl2. Intracellular calcium transients were measured using an Olympus FV1000 confocal microscope. Peak intracellular Ca2+ was quantified during intracellular release or extracellular Ca2+ influx. D. HMGB1-induced permeability was inhibited by STIM1 knockdown. EA.hy926 cells were plated in the upper part of transwell chambers until the formation of a tight monolayer, then transfected with STIM1 siRNA-1, siRNA-2 or control (scrambled) siRNA. HMGB1 200 ng/ml was added and cells were incubated for an additional 24 h. After incubation, endothelial permeability was assessed, as described above. E. Representative immunoblots showing that STIM1 knockdown inhibits Src activation. Transfected cells were treated with or without 200 ng/ml HMGB1 for 2 h. Cell lysates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by western blotting using antibodies against phosphorylated Src and Src. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *Indicates significant difference compared with the control group (P<0.05).