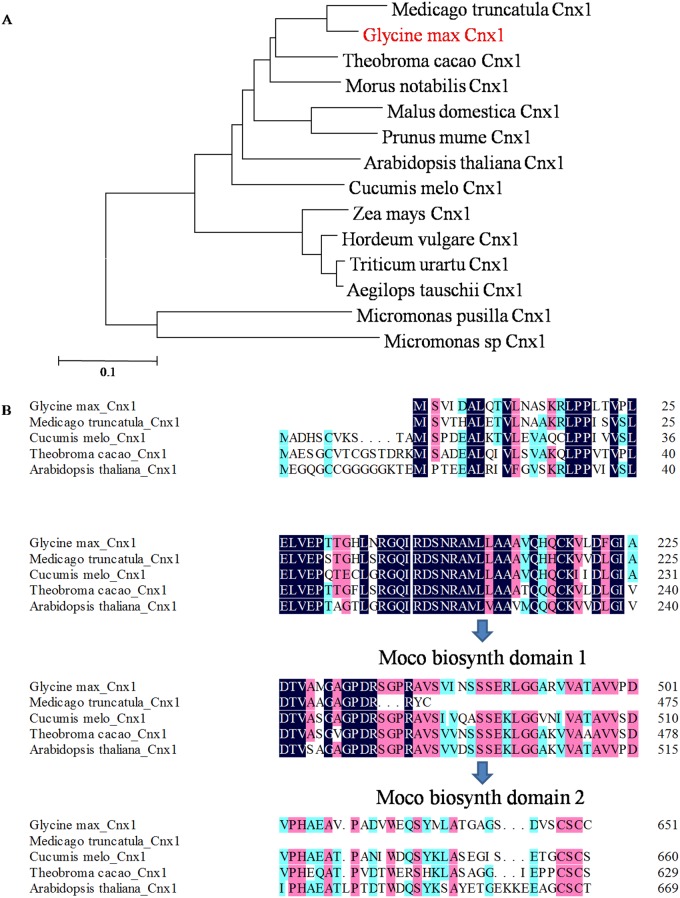
Fig 1. Phylogenetic tree of GmCnx1 gene and alignment of amino acid residues from different species.
(A) Phylogenetic tree constructed by multiple sequence alignments of the Glycine max Cnx1 and those of other Cnx1 proteins. The sequences used are: Medicago truncatula Cnx1, Theobroma cacao Cnx1, Morus notabilis Cnx1, Malus domestica Cnx1, Prunus mume Cnx1, Arabidopsis thaliana Cnx1,Cucumis melo Cnx1,Hordeum vulgare Cnx1, Zea mays Cnx1, Triticum urartu Cnx1, Aegilops tauschii Cnx1, Micromonas sp Cnx1 and Micromonas pusilla Cnx1(Accession nos AET00019, EOY33170, EXB53803, XP_008385638, XP_008231326, EEH56197, XP_008451034, AAF73075, ABB30174, EMS55337, EMT03164, ACO61591 and AED92917.1, respectively). (B) Through the analysis of two Moco domains and alignment of amino acid residues, encoding protein sequences of GmCnx1, Medicago truncatula Cnx1, Cucumis melo Cnx1, Theobroma cacao Cnx1 and Arabidopsis thaliana Cnx1 had high sequence similarity.