Fig 2. a-e. Effects of physical activity on clinical performance.
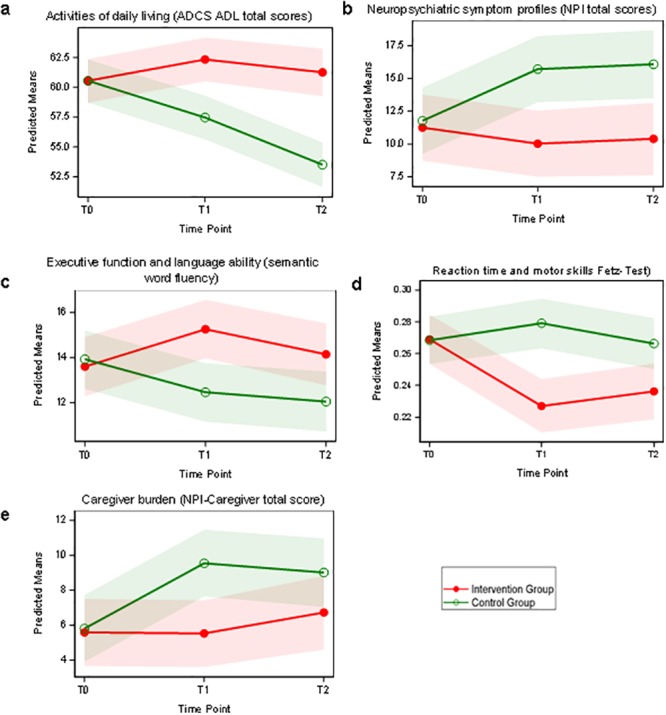
This figure shows the effects of physical activity on the patients when compared to the control group for the three time points (T0- baseline, T1–3 months later or after completion of the intervention and T2- 3 month follow-up). Activities of daily living (ADCS ADL total scores): patients in the control group experienced significant decreases in their performance over 12 weeks and at the 3 month follow-up whereas patients in the intervention group remained stable during the study period and follow-up (Fig 2a). Neuropsychiatric symptom profiles (NPI total scores): controls suffered a considerable increase in behavioural changes over 24 weeks whereas patients in the intervention group remained stable over 24 weeks (Fig 2b). Executive function and language ability: patients in the intervention group improved during the intervention period and returned to initial performance after completion but without revealing the continuous worsening over 24 weeks demonstrated in the controls (Fig 2c). Reaction time, hand-eye quickness and attention (FETZ-test or Ruler Drop Test): only patients in the intervention group improved their performance during the study period (Fig 2d). Caregiver burden (NPI): burden increased in the control group during the first 3 months whereas caregiver burden remained stable in the intervention group during the study period (Fig 2e).
