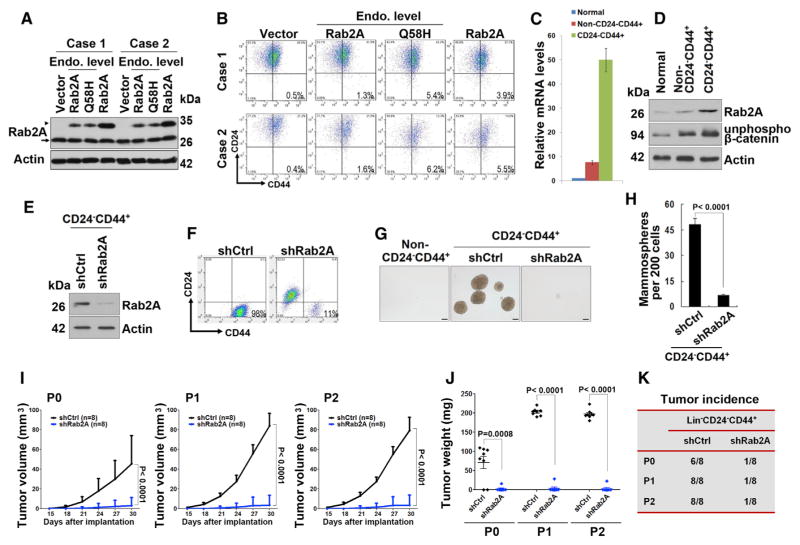
Figure 6. Rab2A and Its Q58H Mutant Endow BCSC Traits to Normal Primary Human MECs, whereas Silencing Rab2A Inhibits Primary Human BCSC Expansion and Tumorigenesis.
(A) Western blot showed lentivirus-mediated overexpression of Rab2A and Q58H mutant in two cases of human normal Lin− MECs. Arrowhead, exogenous Flag tagged protein; arrow, endogenous protein.
(B) Rab2A or Rab2A Q58H mutant increased the CD24−CD44+ population in primary human MECs.
(C) Real-time PCR showed that expression of Rab2A mRNA was markedly increased in the Lin−CD24−CD44+ population, compared to Lin−non-CD24−CD44+ or normal epithelial cells.
(D) Expression of Rab2A and unphosphorylated β-catenin protein was markedly increased in Lin−CD24−CD44+ cells compared to Lin−non-CD24−CD44+ cells in human breast cancer tissue and those in normal breast tissue from the same patient.
(E) Rab2A was knocked down in Lin−CD24−CD44+ cells sorted from human breast cancer tissue.
(F) Rab2A KD in Lin−CD24−CD44+ breast cancer cells decreased the CD24−CD44+ population.
(G and H) Rab2A KD in Lin−CD24−CD44+ breast cancer cells decreased mammosphere formation. Scale bar represents 100 μm.
(I–K) Rab2A KD interfered with both tumor initiation and growth of primary BCSCs in vivo, as shown by tumor growth curve (I), tumor weights (J), and tumor incidence (K). 2,000 lentivirus-transduced Lin−CD24−CD44+ cells isolated from eight breast cancer patients were serially transplanted as xenografts into eight nude mice. P0, freshly isolated primary cells; P1, passage 1; P2, passage 2.
In (C) and (H), error bars represent SD of three independent experiments. In (I) and (J), error bars represent SD of eight mice. See also Figure S6.