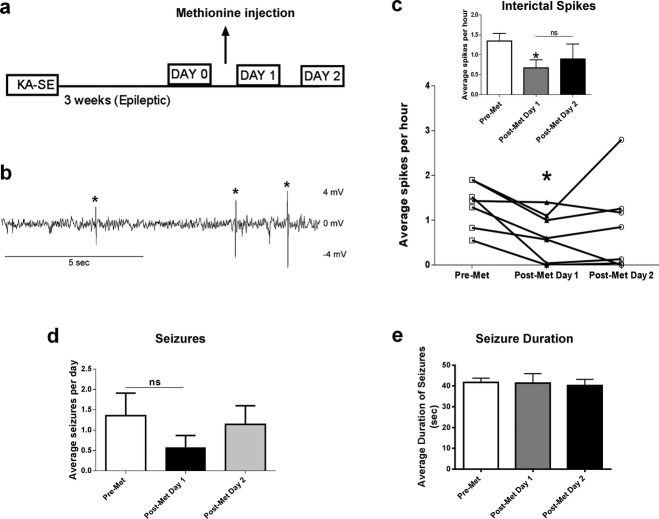
Figure 4.
Methyl supplementation decreases interictal spiking. (a) Diagram of experimental setup. (b) Representative trace of interictal spikes observed in epileptic rats 3 weeks post-KA administration (* represents what was counted as a spike). (c) Methyl supplementation significantly reduced interictal spike number in the first 24 h postinjection. Interictal spiking rate showed a trend toward returning back to baseline at 24–48 h post-Met supplementation (F2,6 = 4.06, P < 0.05, n = 7, one-way analysis of variance [ANOVA] with post hoc test, *significance relative to pre-Met). (d) Methyl supplementation did not have a significant effect on number of seizures per day (F2,18 = 0.82, P > 0.05, n = 7, one-way ANOVA with post hoc test). (e) Methyl supplementation did no significantly affect duration of seizures (F2,23 = 0.91, P > 0.05, n = 3–16, one-way ANOVA with post hoc test, ns = not significant). Error bars are SEM.