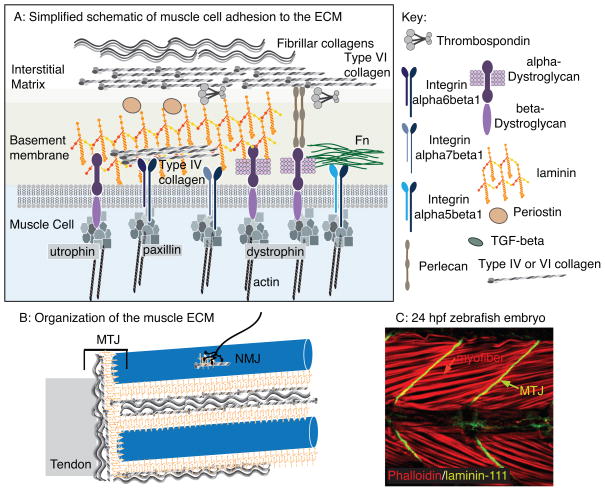
Figure 1.
The muscle ECM. A: Simplified cartoon of proteins involved in muscle cell adhesion to the ECM. Multiple transmembrane receptor complexes indirectly link the intracellular cytoskeleton to the ECM. The BM attaches to the collagen-rich interstitial matrix. B: Larger size scale view of the organization of muscle ECM. Not only are individual muscle fibers encased by ECM, but there are also specialized matrices that define the neuromuscular and myotendinous junctions (NMJ and MTJ, respectively). C: A 24 hpf zebrafish embryo stained with phalloidin (red) to visualize actin and an antibody against laminin-111 (green). Side view, anterior left, dorsal top. Note the long muscle cells (red arrow) that connect to laminin-111 at the myotome boundaries (green arrow). These boundaries will generate the MTJ.