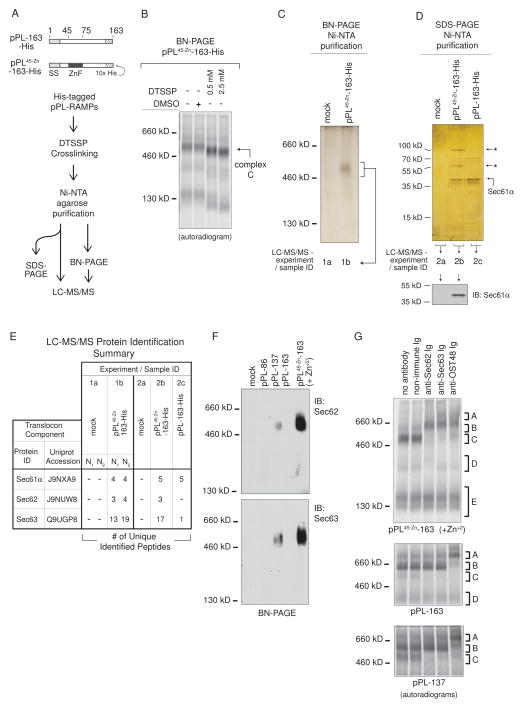
Figure 5. RAMP Complex C Contains Sec61, Sec62, and Sec63.
(A) Purification scheme used to isolate and identify pPL-bound RAMP components. “-His” refers to truncations encoding a 10x His-tag. In panels (B)–(E), all RAMPs were derived from translations in the presence of Zn+2. (B) BN-PAGE of pPL45-Zn-163-His RAMPs treated with DMSO or DTSSP. (C) BN-PAGE (silver stain) of pPL45-Zn-163-His RAMP purifications confirmed complex C isolation. (D) SDS-PAGE of purified pPL45-Zn-163-His RAMPs, compared to those of mock control and pPL-163-His, indicated isolation of 55 and 100 kD proteins (top, silver stain, “←*”). Western blot (bottom) identified the 38 kD band as Sec61α. (E) Samples from experiment 1 and 2, as prepared and designated in panels C and D, were analyzed by LC-MS/MS. Translocon components identified in pPL45-Zn-163-containing samples (1b and 2b) are listed along with numbers of peptide matches, as compared to those identified in mock control (1a and 2a) or pPL-163-His (2c) purified RAMP samples. N1 and N2 are analyses of repeated experiments performed on different days. (F) Western blots confirmed complex C generated from pPL-137 and pPL45-Zn-163(+Zn+2) (ie pPL45-Zn-163 translated in the presence of Zn+2) contained Sec62 and Sec63. (G) Gel-shifts of complex C derived from pPL45-Zn-163(+Zn+2), pPL-163, and pPL-137 translations with indicated antibodies. See also Figure S4 – 6.