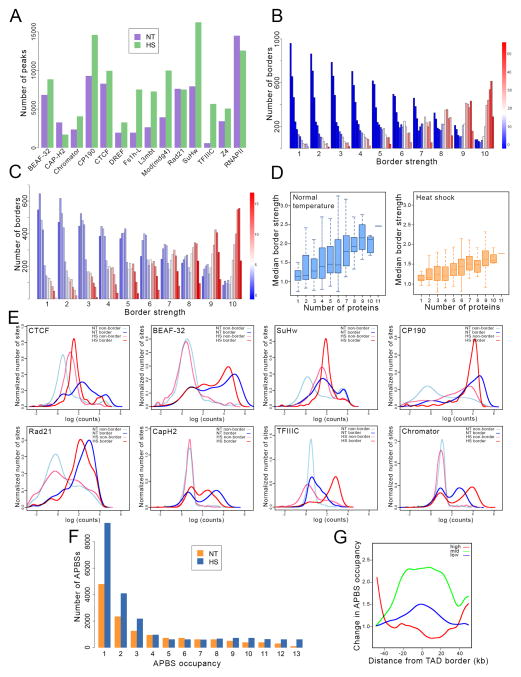
Figure 3. Genome-wide redistribution of architectural proteins during heat shock.
(A) Number of ChIP-seq peaks for different architectural proteins and RNAPII in control (NT) and heat shocked (HS) cells.
(B) Number of borders found in Hi-C data from control cells for each border strength, which ranges from 1 to 10 in arbitrary units. For each border strength, the number of borders containing different amounts of RNAPII (red to blue) and APBSs occupied with different numbers of architectural proteins (12 columns for each border strength ranging in occupancy from 1 to 12 from left to right). Color bar for RNAPII indicates number of mapped ChIP-seq reads in 50 bp bins normalized relative to the total number of reads.
(C) Number of borders found in Hi-C data from heat shocked cells for each border strength, which ranges from 1 to 10 in arbitrary units. For each border strength, the number of borders containing different amounts of RNAPII (red to blue) and APBSs occupied with different numbers of architectural proteins (12 columns for each border strength ranging in occupancy from 1 to 12 from left to right).
(D) Box plots indicating the relationship between median border strength and the number of architectural proteins present at each border for control (left) and heat shocked (right) cells.
(E) Relationship between the normalized number of sites in the genome and the number of normalized ChIP-seq reads for different architectural proteins at TAD borders and non-borders in control and heat shocked cells.
(F) Change in the number of architectural protein binding sites (APBSs) with different numbers of architectural proteins (APBS occupancy) in heat shocked (HS) with respect to control (NT) cells.
(G) Changes in APBS occupancy with respect to the distance from TAD borders for TAD borders with low (1–4) mid (5–8) and high (9–13) number of architectural proteins in heat shocked cells with respect to control.