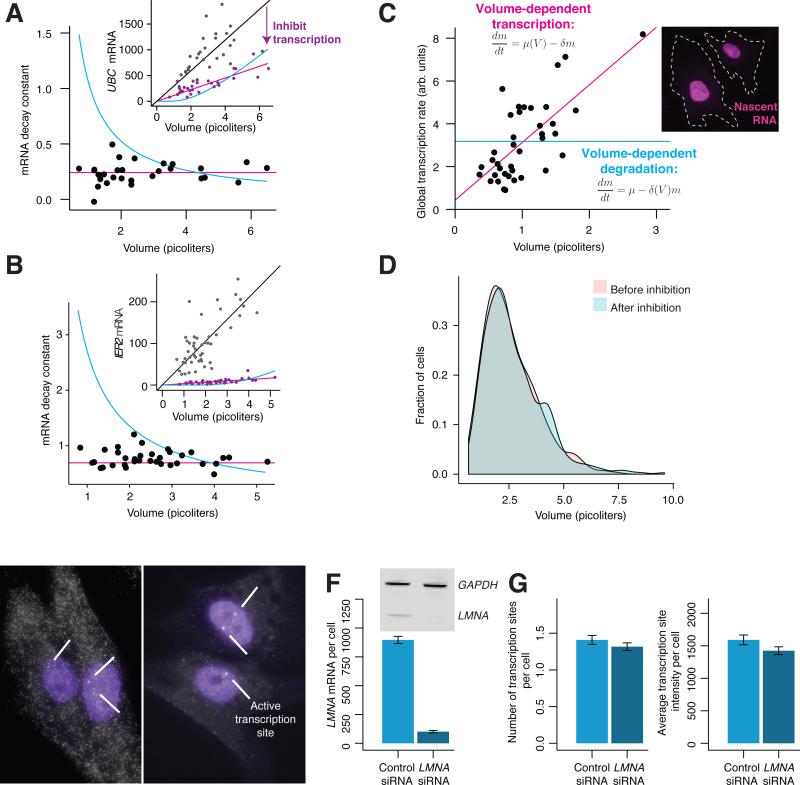
Figure 3. Cells exhibit global volume-dependent transcriptional control over mRNA abundance.
A, B. We inhibited transcription in primary fibroblast cells using Actinomycin D for 4 hours and allowed UBC (A) and IER2 (B) mRNA to degrade. Inset shows mRNA before and after inhibition. Each point represents a single-cell measurement. We calculated the decay constant for each cell using the best-fit line before inhibition (see Methods). Blue line shows fit if degradation were volume-dependent; red line shows fit if transcription were volume-dependent. Data represent one of two biological replicates. C. We fluorescently labeled nascent RNA produced in one hour using the Click-iT eU assay in primary fibroblast cells, and quantified the total fluorescence intensity by imaging the nuclei of single cells. Inset shows raw micrograph data. Blue line shows fit for volume-dependent degradation; red line shows fit for volume- dependent transcription. Data shown is from quiescent cells, and is one of three biological replicates. D. Distribution of cell volumes before and after transcription inhibition. E. We performed siRNA treatment for 72 hours in primary fibroblast cells using either a control siRNA (left), or an siRNA targeting LMNA mRNA (right). DAPI stain is shown in purple, and LMNA mRNA FISH probe is shown in white. White arrows indicate active transcription sites. F. Quantification of cytoplasmic LMNA mRNA knockdown by RNA FISH. Inset shows protein knockdown. G. Comparison of the number of LMNA transcription sites and transcription site intensity in siRNA control and LMNA knockdown conditions. We detected transcription sites through intron/exon colocalization using RNA FISH. All error bars represent standard error of the mean. Data in D, E are a combination of two biological replicates, n = 323 cells for control siRNA, 284 cells for LMNA siRNA.