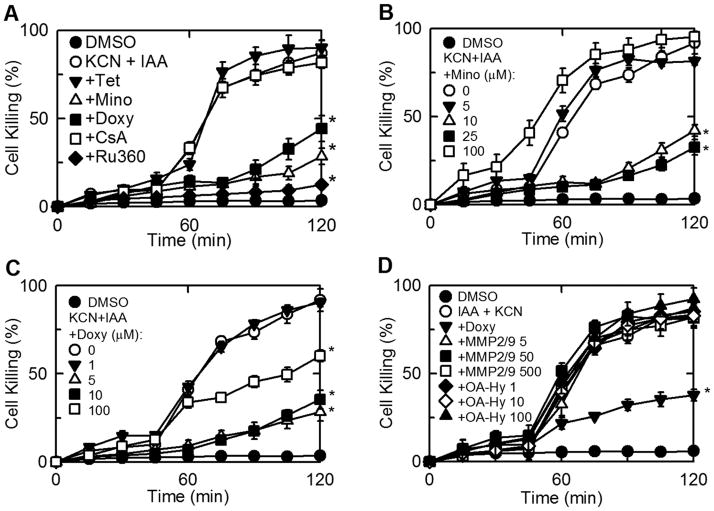
Fig. 1. Chemical hypoxia-induced killing of hepatocytes: protection by minocycline, doxycycline and Ru360 but not by other tetracycline derivatives, cyclosporin A, or matrix mettaloprotease inhibitors.
Cultured rat hepatocytes were treated with (A) tetracycline (Tet, 50 μM), minocycline (Mino, 50 μM), doxycycline (Doxy, 50 μM), CsA (2 μM), Ru360 (100 nM), vehicle (DMSO), (B) minocycline (0–100 μM), (C) doxycycline (0–100 μM), or (D) matrix metalloproteases MMP2/MMP9 Inhibitor 1 (5–500 μM) and cis-9-octadecenoyl-N-hydroxylamide (OA-Hy, 1–100 μM) 30–60 min prior to addition of 500 μM iodoacetic acid (IAA) plus 1 mM KCN (chemical hypoxia). Cell killing was determined by PI fluorometery. Filled circles are DMSO-treated cells not exposed to IAA and KCN. Values are means ± SE from 4 or more experiments. *p ≤ 0.05 versus KCN + IAA.