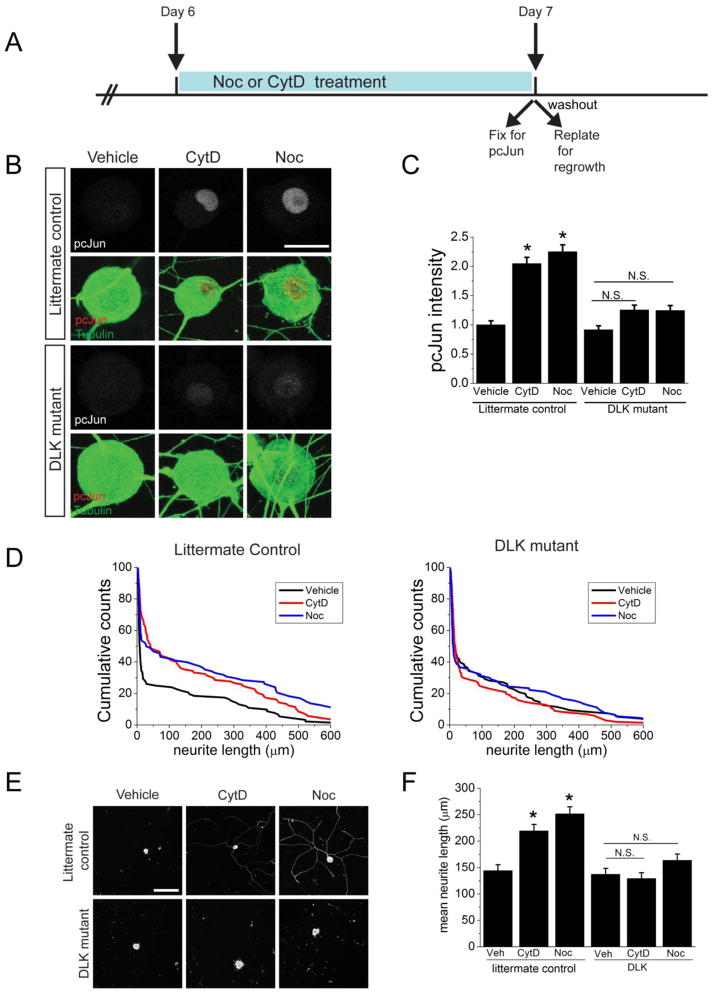
Figure 7. Induction of pcJun and the pro-regenerative program by cytoskeletal disrupting agents requires DLK.
A. Schematic diagram outlining the adult DRG culture experiment. Drugs are present before the replating and are washed out for the regrowth phase.
B. Sample confocal images of adult DRG neurons cultured for 7 days. At DIV 6, neurons were treated for 24 hours with vehicle, cytochalasin D (CytD) or nocodazole (Noc). Cells are stained for pcJun (red) and β3 tubulin (green) at the end of the drug treatment. Littermate controls (DLKF/F); DLK mutant (DLKF/F, Adv-Cre). Scale bar = 10 μm.
C. Quantification of the pcJun intensity in the groups represented in B and normalized to vehicle-treated condition for each genotype. *p<0.05, N.S. = not significant. Over 150 neurons/condition derived from 3 different mice for each genotype were analyzed.
D. Pretreatment with cytochalasin D and nocodazole significantly increases neurite outgrowth in control but not in the DLK mutant mice. Representative cumulative distribution plots for the longest neurite per cell from one mouse of each genotype 18 hours after replating. Littermate controls (DLKF/F); DLK mutant (DLKF/F, Adv-Cre). ~100 neurons were measured for each condition.
E. Sample confocal images of replated DRG neurons on day 7 after pretreatment with vehicle, cytochalasin D or nocodazole. Neurons were replated and allowed to grow for 18 hours in the absence of drug in each condition. The relative paucity of neurites is due to the reduced ability of the neurons to regrow axons after replating on day 7 in culture. Littermate controls (DLKF/F); DLK mutant (DLKF/F, Adv-Cre). Scale bar = 100 μm.
F. Mean neurite length for each of the conditions represented in D and E. *p<0.05. n=3 mice for each genotype.