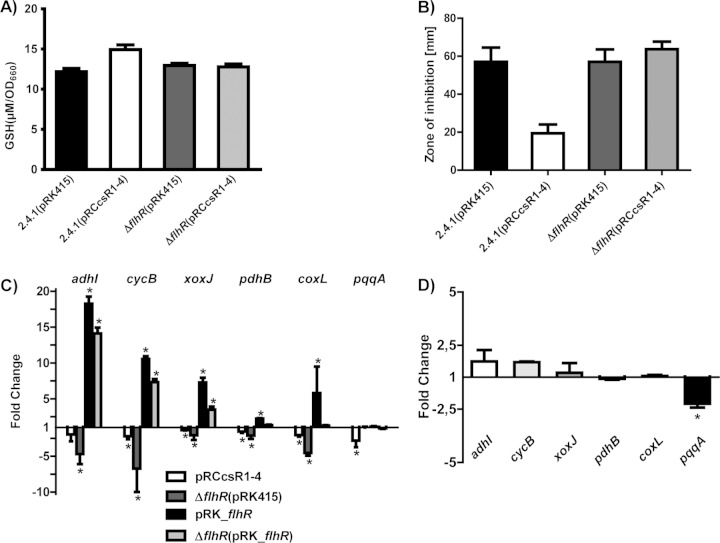
FIG 5.
Comparison of CcsR1–4 functions in the wild-type and flhR deletion backgrounds. (A) Intracellular GSH was measured in wild-type 2.4.1 and an endogenous flhR deletion strain overexpressing CcsR1–4 (pRCcsR1–4), as well as in the respective control strains carrying the empty vector pRK415. The GSH concentration was determined in cell extracts from cultures in the exponential growth phase and normalized to the OD660. The error bars indicate the standard deviation from the mean of biological triplicates with two technical replicates. (B) Enhanced resistance to oxidative stress promoted by CcsR1–4 overexpression is not observable in the endogenous flhR deletion strain, as demonstrated by zone-of-inhibition assays. Filter disks soaked with 700 mM tBOOH were placed on soft agar plates to suppress bacterial growth. Wild-type R. sphaeroides and an endogenous flhR mutant strain carrying plasmid pRK415 or pRCcsR1–4 were compared. After 3 days of incubation, the diameters of the zones of inhibition were measured. Results represent the mean and error bars indicate the standard deviation for three independent biological replicates. (C) Expression of selected genes from C1 metabolism and pdhB determined by qRT-PCR in wild-type R. sphaeroides carrying the plasmid pRCcsR1–4 and in an endogenous flhR deletion strain. Moreover, wild-type R. sphaeroides carrying the plasmid pRK_flhR and the endogenous flhR deletion strain carrying the plasmid pRK_flhR were compared to wild-type R. sphaeroides carrying the empty plasmid pRK415. (D) CcsR1–4 overexpression in the flhR deletion strain does not lead to significantly changed expression of pdhB and most selected genes of C1 metabolism, while only pqqA shows decreased expression, as determined by qRT-PCR. The error bars indicate the standard deviation of the mean of three biological replicates consisting of two technical replicates each. Asterisks indicate a statistically significant change in gene expression (P ≤ 0.05).