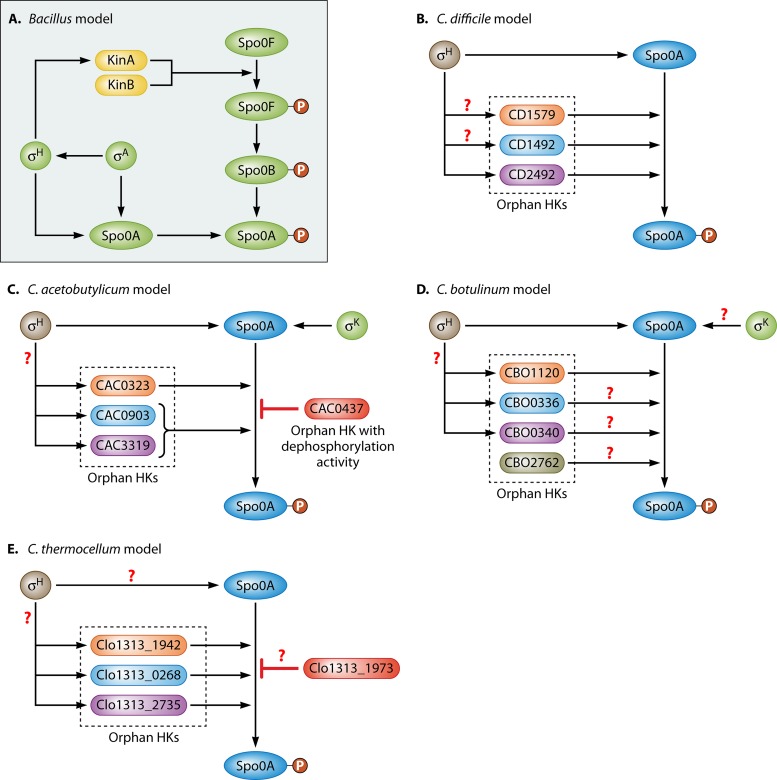
FIG 2.
Activation of Spo0A via phosphorylation in B. subtilis (A), C. difficile (B), C. acetobutylicum (C), C. botulinum (D), and C. thermocellum (E). In Bacillus, the phosphorylation process is initiated once the orphan HKs KinA and/or KinB phosphorylates Spo0F, the first component of the phosphorelay system that leads to Spo0A phosphorylation. Based on all Clostridium organisms sequenced so far, there is no evidence that they have a recognizable phosphorelay system. Instead, several orphan HKs were shown to directly transfer a phosphate group to Spo0A, thus activating it. Additionally, it was shown that the orphan HK CAC0437 in C. acetobutylicum has dephosphorylation activity and is thus able to remove the phosphate group from Spo0A, thus rendering it inactive. Clo1313_1973 in C. thermocellum may also have the ability to inactivate Spo0A, although direct evidence of dephosphorylation activity has yet to be obtained.