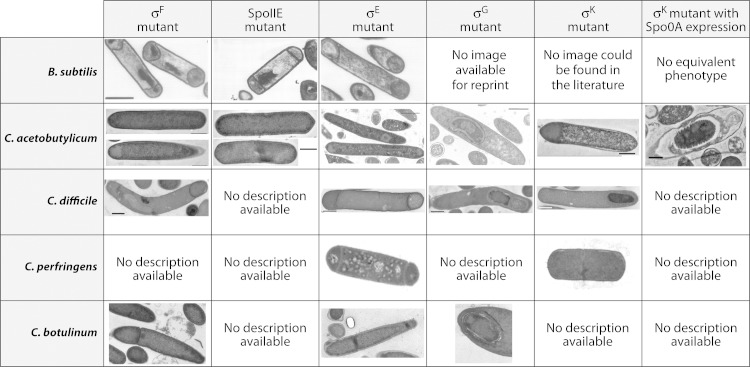
FIG 5.
TEM images comparing the various sporulation-specific sigma factor mutants generated in B. subtilis and Clostridium organisms, including C. acetobutylicum, C. difficile, C. perfringens, and C. botulinum. In the sigK deletion mutant of C. acetobutylicum, sporulation was blocked prior to stage II, which is also true for the C. acetobutylicum sigF, spoIIE, and sigE disruption mutants as well as the sigK mutant of C. perfringens. However, the sigK mutant of C. difficile appeared to progress further in sporulation, and a developing forespore appears to be present. On the other hand, the sigF, spoIIE, and sigE disruption mutants of B. subtilis were all able to develop asymmetric septa and exhibited a disporic phenotype. The sigG disruption mutant generated in C. acetobutylicum appeared to progress further into the sporulation pathway than its counterpart in B. subtilis due to the presence of what appears to be a spore coat and cortex, which were not visible in the sigG mutant of B. subtilis. (For an image of a B. subtilis σG mutant, see Fig. 2 in reference 104.) Expression of Spo0A in the sigK deletion mutant of C. acetobutylicum showed that the cells were able to progress further in spore morphogenesis than the sigG mutant; however, they were still unable to form viable spores, and the spore coat and cortex appeared to be ill formed, thus indicating that σK is also needed during the last stages of sporulation. (Images of the B. subtilis σF mutant, SpoIIE mutant, and σE mutant reprinted from reference 91 with permission; image of the C. acetobutylicum σF mutant reprinted from reference 88; image of the C. acetobutylicum SpoIIE mutant reprinted from reference 115; images of the C. acetobutylicum σE mutant and σG mutant reprinted from reference 26; image of the C. acetobutylicum σK mutant reprinted from reference 66; images of the C. difficile σF mutant, σE mutant, σG mutant, and σK mutant reprinted from reference 25; images of the C. perfringens σE mutant and σK mutant reprinted from reference 63 with permission; images of the C. botulinum σF mutant, σE mutant, and σG mutant reprinted from reference 96 with permission.)