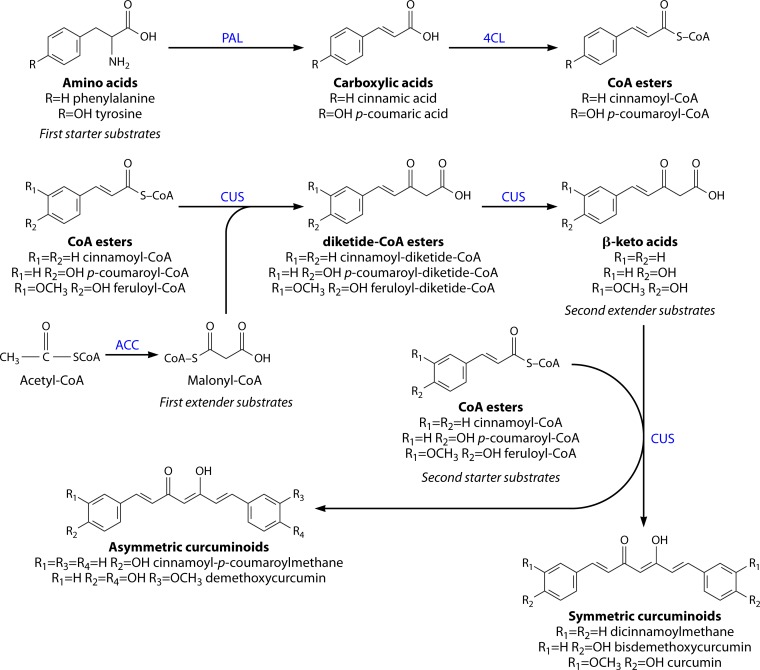
FIG 3.
Biosynthesis of curcuminoids by recombinant Escherichia coli, using tyrosine and/or phenylalanine as starter substrates that are converted to carboxylic acids by PAL (phenylalanine ammonia lyase). The carboxylic acids, which can also be added directly to the medium, are converted into the corresponding CoA esters by 4CL (4-coumarate-CoA ligase) (top), which is followed by several reactions catalyzed by curcuminoids synthase (CUS) (bottom). Malonyl-CoA is overproduced by ACC (acetyl-CoA carboxylase). (Adapted from references 106 and 100.)