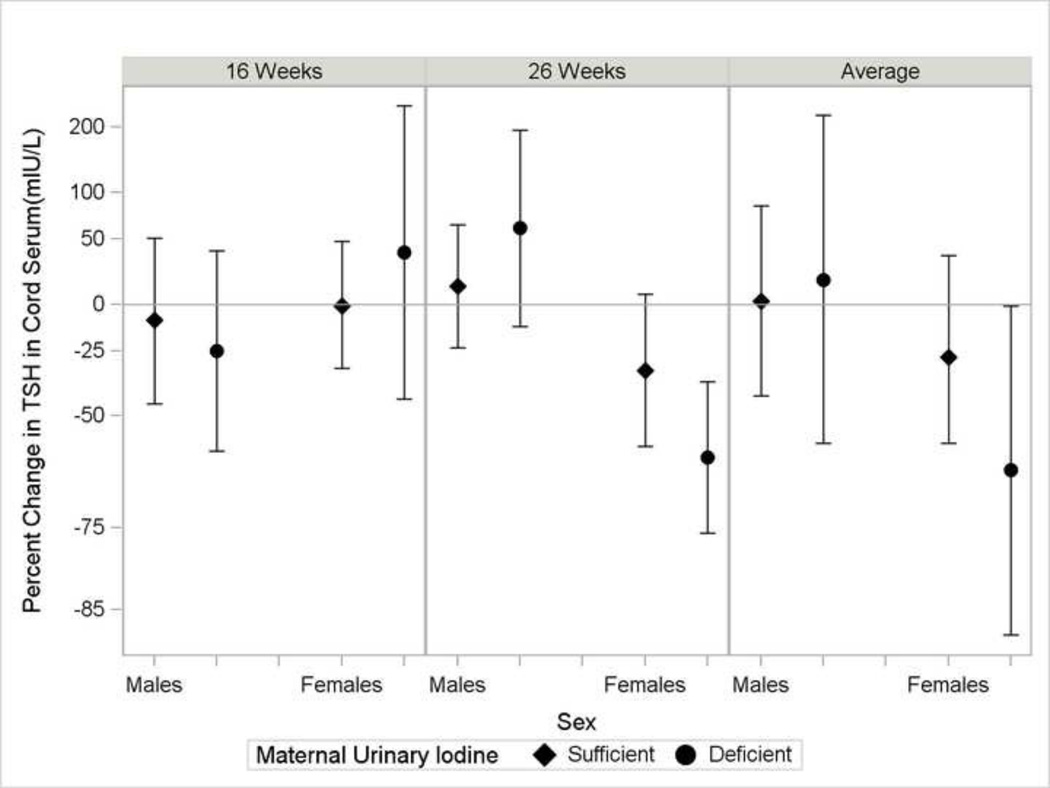
Figure 1.
Percent change in thyroid stimulating hormone concentrations in cord serum (n=193) with 10-fold increase in maternal urinary BPA in the Health Outcomes and Measures of the Environment Study by newborn sex and iodine deficiency. Sufficient iodine was defined by maternal urinary iodine ≥150 µg/g creatinine (diamond marker) and deficient iodine as maternal urinary iodine <150 µg/g creatinine (circle marker). Percent change calculated as eβ −1×100, where β=coefficient from a multivariable linear regression model including adjustment for maternal age, race, education, alcohol consumption, smoking, parity, prenatal vitamin use, Log10-polychlorinated biphenyl 153, delivery by Cesarean section, gestational week at delivery, newborn sex, iodine insufficiency, and product terms for bisphenol A by newborn sex, bisphenol A × iodine deficiency, newborn sex × iodine deficiency, and a bisphenol A × newborn sex × iodine deficiency. From left to right, the panels represent estimates from log10-transformed creatinine-standardized bisphenol A in maternal urine at 16 weeks, 26 weeks, and the average of the log10-transformed creatinine-standardized bisphenol A from maternal urine collected at the 16 and 26 week visits urine