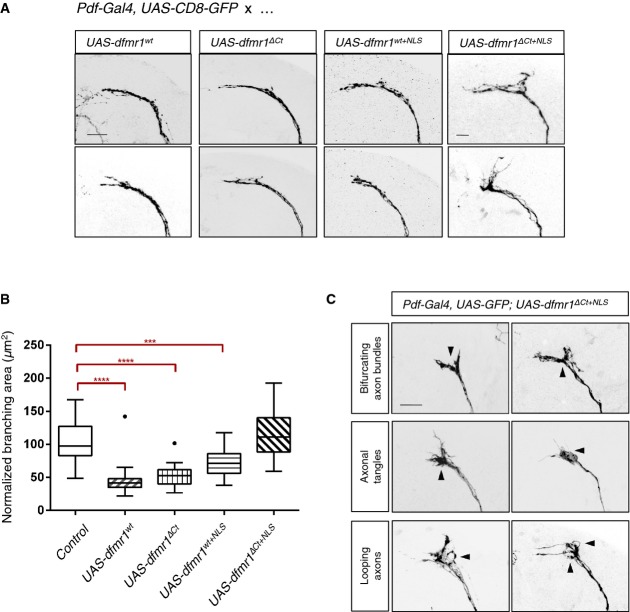
Figure 6. Compound effects of the patient mutation confer a neomorphic function for Dfmrp in sLNV neurons.
- Overexpression of wild-type dfmr1 (UAS-dfmr1wt) using a LNv neuron-specific driver line (Pdf-Gal4) causes reduction of branching area—“axonal collapse”—in the sLNv axonal termini. dfmr1ΔCt and dfmr1wt+NLS overexpression phenocopies overexpression of dfmr1wt, suggesting that the truncation of the C-terminus or the presence of the patient NLS alone does not impair or alter the functional efficacy of dfmr1 in this context. However, overexpression of dfmr1ΔCt+NLS fails to cause collapse of sLNv termini, indicating a significant loss or change of Dfmrp protein function. Axonal morphology is visualized by expressing CD8-GFP under the control of the same neuronal driver. Scale bar represents 10 μm.
- Quantification of axonal termini branching in LNv neurons overexpressing various dfmr1 alleles. Overexpression of dfmr1wt, dfmr1ΔCt, or dfmr1wt+NLS significantly reduced axonal branching area [****P < 0.0001; control 101.3 ± 29.76 SD, n = 30; UAS-dfmrwt 45.41 ± 21.69 SD, n = 29; UAS-dfmrΔCt 52.31 ± 14.67 SD, n = 32; UAS-dfmrwt+NLS 72.45 ± 21.83 SD, n = 29; UAS-dfmrΔCt+NLS 117.8 ± 36.96 SD, n = 28]. dfmr1ΔCt+NLS overexpression does not result in a significant change of axonal branching area compared to the background control [Pdf-Gal4, UAS-GFP] (P = 0.672). For quantification purposes, each branching area (n) was manually outlined, starting from the first point of defasculation of the axonal bundle. These measurements were normalized for variability in brain size across samples using LNv commissure length measurements for each brain. Two-tailed t-tests using Welch's correction were then used to compare controls with mutant phenotypes (GraphPad). Error bars represent mean values with SD. Dots visible for box plots of UAS-dfmrwt and UAS-dfmrΔCt represent samples that outlier the whiskers.
- Overexpression of dfmr1ΔCt+NLS results in aberrant axonal termini morphology. Axonal guidance defects were frequently observed (arrowheads) and scored manually for bifurcations of the axon bundle (9/48), tangling of axons in the termini (13/48), and apparent looping of axons (7/48).