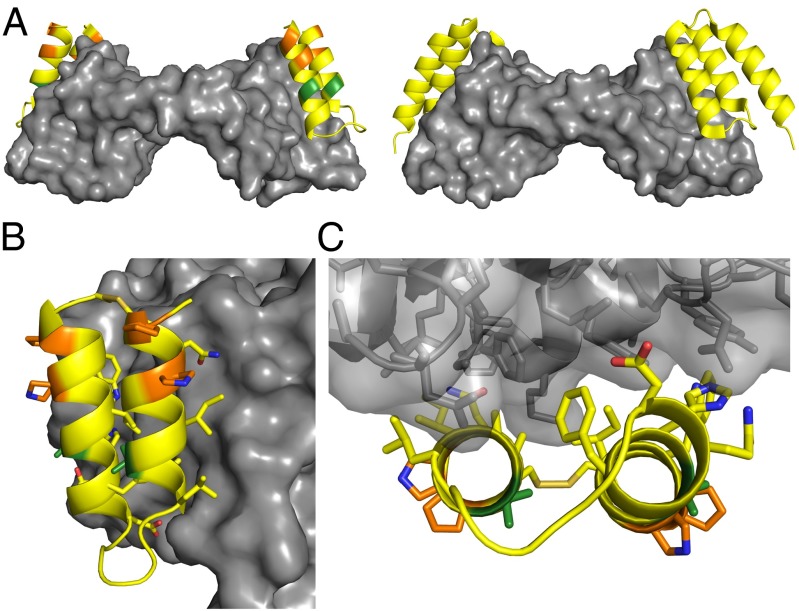
Fig. 3.
Crystal structure of α/β-VEGF-1 in complex with VEGF8–109. Residues in α/β-VEGF-1 are colored by type of residue (yellow for α, green for Aib, and orange for cyclic β). VEGF8–109 is depicted as a gray surface. (A, Left) Cartoon representation of α/β-VEGF-1 bound to VEGF8–109. (Right) Cartoon representation of α-peptide Z-VEGF bound to VEGF8–109 (PDB ID code 3S1K) (19), for comparison. The α/β-peptide binds to the same surface of VEGF8–109 as Z-VEGF. (B) Side view of α/β-VEGF-1+VEGF8–109 highlighting the interface between these molecules. The side chains are displayed as sticks for residues of α/β-VEGF-1 appearing to make contact with VEGF8–109, for Aib and cyclic β-residues, and for the disulfide bond. Carbon atoms are colored by residue type, blue atoms are nitrogen, red atoms are oxygen, and tan atoms are sulfur. (C) View of the α/β-VEGF-1+VEGF8–109 interface looking along the α/β-peptide helical axes. VEGF8–109 shown as transparent surface with cartoon backbone and side chains represented as sticks.