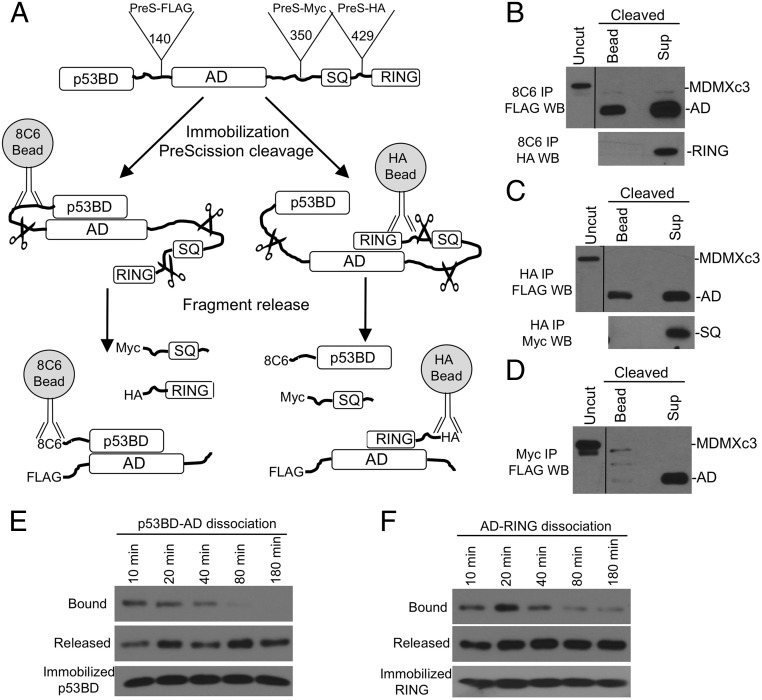
Fig. 2.
Proteolytic fragment release (PFR) assay. (A) Diagram of PFR assay for MDMX intramolecular interactions. MDMXc3 was immobilized on beads by using different antibodies and cleaved by PreScission for <40 min. The beads and supernatant were analyzed by Western blot to detect fragment release from the beads. (B) MDMXc3 expressed in H1299 was immobilized on 8C6 beads (captures MDMXc3 through the p53BD fragment) and incubated with PreScission for 40 min. The beads and supernatant were analyzed by FLAG and HA Western blot. The presence of AD fragment in the bead fraction indicates slow dissociation from the immobilized p53BD. Absence of RING fragment in the bead fraction indicates lack of binding to the p53BD. (C) Immobilization of MDMXc3 through the RING domain revealed RING binding to AD but not SQ fragment. (D) Immobilization of MDMX through the SQ fragment revealed lack of binding to the AD. (E) MDMXc3 captured on 8C6 beads was cleaved with PreScission in <5 min. Beads and supernatants were separated at indicated time points and analyzed by FLAG Western blot to detect the dissociation of AD from p53BD. (F) MDMXc3 immobilized using HA antibody was analyzed for the dissociation of AD from RING after cleavage at indicated time points.